IMF head laments 'loss of momentum' in financial reform!
Search Results
-
India's Debt Situation | Economy Watch
India's debt situation focuses on the total amount of external debts taken by ... India and the Global Economy · World Bank Lending To India's Health Sector ...
www.economywatch.com › Indian Economy - Cached - Similar -
India - Data & Statistics
- [PDF]
External Debt 6.82 India's external debt at US$ 123.3 billion at ...
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat
factors, India's external debt increased further ... Finance 2005, World Bank (Table 6.15). 6.84. The external debt management policy ...
www.indiabudget.nic.in/es2005-06/chapt2006/chap618.pdf -
World Bank Speak Out: India's total debt burden is high, although ...
-
World Bank Speak Out: Interview with Vikram Nehru on Debt - Is it ...
- [PDF]
India at a glance
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
India at a glance. 12/9/09. Lower-. POVERTY and SOCIAL. South middle-. India. Asia income. 2008. Population, mid-year (millions) ... Total debt/GDP. 21.0. 23.7. 17.4. 19.9. Total debt service/exports .... World Bank program. Commitments ...
devdata.worldbank.org/AAG/ind_aag.pdf - Similar -
I AM WARM – World Bank In India By Bharti Patel
-
The World Bank and India : Chapter 10
-
how much india's loan in world bank? ? - Yahoo! Answers India
13 Nov 2008 ... India owes $230.85 billion to the external world as debt as on December ... about india, which india has to pay world bank,.....but India is ...
in.answers.yahoo.com › ... › International Organizations - Cached - Similar -
South Asia - Data & Statistics
The prevalence of underweight children in India is among the highest in the world, ... Summaries of World Bank lending and debt service in the region: ...
web.worldbank.org/.../0,,menuPK:158851~pagePK:146732~piPK:146813~theSitePK:223547,00.html - Cached
-
'Tweak rules to tap long-term debt for infra fund'
The Hindu - 8 Jun 2010
The panel on the infrastructure debt fund has also urged the sectoral regulators — the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of ...Allow insurance, pension funds in debt market: panel - Business Standard
Doors may open for foreign investment in infra debt fund - Hindu Business Line
Infrastructure debt gap $50 billion: Parekh panel - Daily News & Analysis
Economic Times - Financial Express
all 36 news articles »
Stock Watch -
Sensex logs longest run since September; gains 50 points
Sify - 1 day ago
World stocks measured by the MSCI All-Country World Index advanced 0.2 per cent ... Top lender State Bank of India, bucked the trend and shed 0.1 per cent. ...Indian shares flip-flop; Reliance Comm jumps - Reuters
BSE Sensex seen up; Reliance, Tata Motors eyed - Reuters India
Banking, IT shares decline in volatile market - BloombergUTV
Equitymaster.com (registration) - Moneylife Personal Finance Magazine
all 515 news articles »
The Hindu -
Markets volatile over Euro zone debt concerns
Economic Times - 5 days ago
Developing nations like India are not affected by this contagion so far due to the ... or 22.91 percent of the world economy, according to the World Bank. ... -
Select side counters sharply higher
BloombergUTV - 10 Jun 2010
State Bank of India, Larsen & Toubro and Reliance Industries edged higher. ... The World Bank on Wednesday said a double-dip recession could not be ruled ...Sensex Crashes By 2% On World Woes - india-server.com
Sensex snaps 3-day rally, falls 337 points - Sify
No end to financial volatility - The Hindu
Press Trust of India - Economic Times
all 621 news articles »
Indian Express -
RIL: In the broadband game
Business Standard - Sunaina Vasudev - Ujjval Jauhari - 3 days ago
According to a World Bank report, a 10 per cent increase in broadband penetration ... impinged by the prospect of rising cost of debt over FY11 and FY12, ...Indian Market Ends Higher For Third Day - Daily Markets
Mergers & Acquisition Round Up - June 07 to June 11, 2010 - India Infoline.com
BusinessWeek - BloombergUTV
all 645 news articles »
Reuters India -
Central banks join gold rush
CNNMoney - 12 hours ago
In the first quarter of 2010, Russia's central bank increased its gold ... The move, which multiplied India's reserves by 55%, was seen as a way for the ...Gold & Silver "Bullish" as Gold's Correlation with Euro ... - BullionVault
all 318 news articles »
Reuters India -
News Roundup: Mukesh Ambani Eyes RCom, Fortis
VC Circle - 1 day ago
The deal may not include Aman's New Delhi property, and, if concluded, will help India's largest real estate company cut its Rs 14000 crore debt pile. ...Market settles at 1-1/2 month high; extends gains for seventh day - BloombergUTV
all 271 news articles »
Reuters India -
Indian microlenders boom but debts rise
Business Report - Ruth David - 1 day ago
In rural India, people are being lent to at 150 percent of the value of their .... Under the bill, the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development ... -
India ETFs Ride High on Robust Economy
TheStreet.com - Don Dion - 16 hours ago
The Reserve Bank of India is likely to raise interest rates soon, ... whereas the developed world's low inflation is the result of too much debt. ... -
Asia should focus on improving domestic demand: ADB
Xinhua - Kristine Liu - Lin Zhi - 20 minutes ago
India, another major growth driver in the region, on the other hand, has reported a ... In its April East Asia and Pacific Economic Update, World Bank ...
-
Palash Biswas Blogs – View Palash Biswas countries regional Blogs ...
-
KOMAL GNDHAR – View Palash Biswas countries regional
11 Nov 2009 ... Indian Holocust My Father`s Life and Time-Two Hundred Five Palash Biswas http://indianholocaustmy fatherslifeandtime.blogs pot.com/ ...
palashbiswas.ibibo.com/Blogs/.../11/.../298878~KOMAL-GNDHAR - Cached -
खोज परिणाम
- [ Translate this page ]MS 13, OBAMA, Unregulated Indian Open Market and FREsenSEX Periphery Economy Troubled Galaxy Destroyed Dreams: Chapter 222 Palash Biswas Most Popular on ...
hindi.mywebdunia.com/search/English/9.html?type=text -
खोज परिणाम
- [ Translate this page ]Face of the RESISTANCE MANIK MANDAL Troubled Galaxy Destroyed Dreams: Chapter 210 Palash Biswas News results for Indian Economy Rate cuts fail to revive ...
hindi.mywebdunia.com/search/US/19.html?type=text -
Palash chandra Biswas's Blog at BIGADDA >> Our claim that Mumbai ...
17 Dec 2009 ... Palash Biswas asks why sachin has to defend Indians in Mumbai ..... themselves in MASTERBASION with the Gandhian Ideology on Indian economy. ...
blogs.bigadda.com/.../our-claim-that-mumbai-terror-strike-is-a-cia-and-mossad-affair-is-proved-as-headly-turns-out-a-cia-agentus-backs-10... - Cached -
Palash chandra Biswas's Blog at BIGADDA >> JATI Hi PUCHHO SADHU KI ...
-
Indian Holocaust My Father`s Life and Time: BUDGET JALAO! BURN The ...
 Rural Mutiny, FARM CRISIS and Cereally challenged Indian Economy  Troubled Galaxy Destroyed Dreams: Chapter 174  Palash Biswas  Indian ADRs lose nearly ...
indianholocaustmyfatherslifeandtime.blogspot.com/.../budget-jalao-burn-budget.html - Cached -
Hegemony Info | Facebook
Palash Biswas Colonial Empire of Emerging Market and Strategic Hamlets and Colonial Hegemony in Colonial Political Economy of Manusmriti Rule Zionist! Indian Holocaust My Father`s Life and Time- Three Hundred Eighty Eight Palash Biswas ...
www.facebook.com/pages/Hegemony/103785472993243?v=desc - Cached -
Bijapur district blogs
Sajan George of the Global Council of Indian Christians said Pastor Paul, 46, ... of Land Acquisition in Singur Threats and opportunities of Iconic Economy, ... in Singur Palash Biswas Contact: Palash C Biswas, C/O Mrs Arati Roy, ...
www.whataboutu.com/blogs_Bijapur+district~10746.html - Cached -
Promoted Inferno:Fire guts Kolkata markets, spreads to multi ...
Contact: Palash C Biswas, C/O Mrs Arati Roy, Gosto Kanan, Sodepur, ...... Economic Zone (SEZ)s are planned to boost the Indian economy - Aimed at sustained ...
indiainteracts.in/.../Promoted-InfernoFire-guts-Kolkata-markets-spreads-to-multistoreys/ - Cached
Sponsored links
|
IMF head laments 'loss of momentum' in financial reform!World leaders' commitment to global reforms of the financial sector is flagging, IMF head Dominique Strauss-Kahn said on Thursday. Meanwhile, Europe clamped down on excessive state borrowing and laid foundations for cross-border economic government on Thursday, as leaders kept a fearful eye on gathering dark clouds over Spain. What about the Nuclear Super Power Brahaminical Nation, Sensex shining India without Fiscal Policy and living on Foreign Capital in an Exclusive Economy where NO Whip seems to Control BORROWING which means Balance of Payment depend on Proactive RBI, Taxation Reloaded against the Purchasing Power deprived Majority Masses, Monopolistic Aggression against the Aboriginal Indigenous Minority Humanscape, Excessive State Borrowing , ForeignCapital Inflow, SELL OFF Nation and Nature, Resources, Economic Ethnic Cleansing, Displacement, Persecution, Exodus, Genocide Culture, Regemented Hegemony, Military Option with Zero Intolerance, Inherent Inequality and Injustice, Holocaust and so on!They used a European Union summit to widen their focus from public overspends and also target dangerously high private sector debt, a bigger problem with Spain's banks than it ever was with bailed-out Greece. What is the agenda of the Extraconstitutional Goverenment of India Incs led by Super Slaves and Remote Controlled by the Zionist Foregn Rooted NRI Dependent Zionist Dynasty?
Seperately Spain and Germany also decided to carry out stress tests on private banks public in a bid to soothe markets.
Diplomats said agreement was reached to toughen sanctions for those who blow their budgets.
But differences remained on how far to go in the creation of new penalties, intended for application after EU president Herman Van Rompuy produces a definitive report on economic governance in October.
These will apply only to those countries that share the euro currency, sources said.
Detailed discussions on whether, for example, the worst offenders could have EU voting rights withdrawn will take place on July 12, when Van Rompuy's "task force" next meets.
By the time specific changes come in, Estonia will also have become the 17th country to switch to the shared currency after the leaders assembled in Brussels gave their green light to entry on January 1.
New British Conservative Prime Minister David Cameron had arrived for his first summit vowing to defend vigorously a series of "red lines," with diplomats warning that penalties going beyond the 16-nation eurozone would require treaty change.
He was not alone in resisting anything that might require painful and uncertain negotiations.
"We already have the solutions and the measures needed," said Swedish Prime Minister Fredrik Reinfeldt, pointing out that existing sanctions have never been used.
"I am sometimes a bit worried about the loss of momentum" in the reform of the financial sector, in face of the "huge" task ahead, Strauss-Kahn told a conference.
Previously, "leaders were very committed to do something in the financial sector but as the crisis vanished, most of them are more concerned by domestic questions," the head of the International Monetary Fund said.
"It would be unfair to say that the momentum has disappeared ... nevertheless I don't see the pressure as big and strong as it was a few months ago," Strauss-Kahn added.
Governments in the United States and Europe have been scrambling to revamp and adapt banking rules since the collapse of US investment bank Lehman Brothers in September 2008 sparked a global credit crunch.
The IMF however has said that more direct measures than those proposed so far are needed, such as levies tied to risk presented by individual banks or limits to the size of their business.
Strauss-Kahn also said he was concerned about the consistency in priorities in financial reform across borders, citing different approaches in the United States and Italy as examples.
"Having an inconsistent system in the biggest economies ... is of course creating new cause for regulatory arbitrage and the trigger for the next crisis.
"The countries having experienced some problems in the financial sector, namely the US and the European countries, are really keen to do something," he said.
However, those countries that have not had major problems in the financial sector, like Canada and some emerging economies, tend to say that major reforms are not needed, he added.
Economy of India
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The economy of India is the eleventh largest economy in the world by nominal GDP[1] and the fourth largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).[9] In the 1990s, following economic reform from the socialist-inspired economy of post-independence India, the country began to experience rapid economic growth, as markets opened for international competition and investment. In the 21st century, India is an emerging economic power with vast human and natural resources, and a huge knowledge base. Economists predict that by 2020,[10] India will be among the leading economies of the world.
India was under social democratic-based policies from 1947 to 1991. The economy was characterised by extensive regulation, protectionism, public ownership, pervasive corruption and slow growth.[11][12][13][14] Since 1991, continuing economic liberalisation has moved the economy towards a market-based system.[12][13] A revival of economic reforms and better economic policy in 2000s accelerated India's economic growth rate. In recent years, Indian cities have continued to liberalize business regulations.[15] By 2008, India had established itself as the world's second-fastest growing major economy.[16][17][18] However, the year 2009 saw a significant slowdown in India's official GDP growth rate to 6.1%[19] as well as the return of a large projected fiscal deficit of 6.8% of GDP which would be among the highest in the world.[20][21]
India's large service industry accounts for 62.5% of the country's GDP while the industrial and agricultural sector contribute 20% and 17.5% respectively. Agriculture is the predominant occupation in India, accounting for about 52% of employment. The service sector makes up a further 34%, and industrial sector around 14%.[22] The labor force totals half a billion workers. Major agricultural products include rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes, cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry and fish.[23] Major industries include telecommunications, textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, information technology enabled services and software.[23]
India's per capita income (nominal) is $1,030, ranked 139th in the world,[24] while its per capita (PPP) of US$2,940 is ranked 128th.[25][26] Previously a closed economy, India's trade has grown fast.[12] India currently accounts for 1.5% of World trade as of 2007 according to the WTO. According to the World Trade Statistics of the WTO in 2006, India's total merchandise trade (counting exports and imports) was valued at $294 billion in 2006 and India's services trade inclusive of export and import was $143 billion. Thus, India's global economic engagement in 2006 covering both merchandise and services trade was of the order of $437 billion, up by a record 72% from a level of $253 billion in 2004. India's trade has reached a still relatively moderate share 24% of GDP in 2006, up from 6% in 1985.[12]
Balance of payments
Since independence, India's balance of payments on its current account has been negative. Since liberalisation in the 1990s (precipitated by a balance of payment crisis), India's exports have been consistently rising, covering 80.3% of its imports in 2002–03, up from 66.2% in 1990–91. India's growing oil import bill is seen as the main driver behind the large current account deficit.[110] In 2007-08, India imported 120.1 million tonnes of crude oil, more than 3/4th of the domestic demand, at a cost of $61.72 billion.[111]
Although India is still a net importer, since 1996–97 its overall balance of payments (i.e., including the capital account balance) has been positive, largely on account of increased foreign direct investment and deposits from non-resident Indians; until this time, the overall balance was only occasionally positive on account of external assistance and commercial borrowings. As a result, India's foreign currency reserves stood at $285 billion in 2008.
Due to the global late-2000s recession, both Indian exports and imports declined by 29.2% and 39.2% respectively in June 2009.[112] The steep decline was because countries hit hardest by the global recession, such as United States and members of the European Union, account for more than 60% of Indian exports.[113] However, since the decline in imports was much sharper compared to the decline in exports, India's trade deficit reduced to 252.5 billion rupee.[112]
Asian stocks mixed as Europe debt worries ease
Investors have been concerned that European nations would have trouble raising money due to worries about defaults but Spain's bond offering, which drew solid demand, was a fillip for markets.
Oil prices, meanwhile, hovered below $77 a barrel. The euro, lifted by Spain's bond sale, was higher against the dollar.
Japan's benchmark Nikkei 225 stock index edged down 7.08 points, or 0.1 per cent, to 9,992.32 and China's Shanghai Composite Index shed 0.3 per cent to 2,552.44. Taiwan's index dropped 0.1 per cent.
Elsewhere, South Korea's Kospi rose 0.1 per cent to 1,708.79 and Australia's S&P/ASX 200 was up 0.5 per cent at 4,551.40. Hong Kong's Hang Seng added 0.6 per cent to 20,264.15.
In New York Thursday, the Dow Jones industrial average edged up 24.71 points, or 0.2 per cent, to 10,434.17 as easing worries over Europe's fiscal crisis offset disappointing US economic data.
In currencies, the dollar fell to 90.90 yen from 90.92 yen in New York late Thursday. The euro rose to $1.2390 from $1.2378 after earlier trading near $1.2400 - the highest in three weeks.
Benchmark crude for July delivery was down 31 cents at $76.48 a barrel in electronic trading on the New York Mercantile Exchange.
Informed opinion is sharply divided about how the next 12 months will play out for the global economy. Given the size of the disaster in the Gulf of Mexico, we suspect that $20 billion may not be enough to compensate all of the people. |
| Mythili Bhusnurmath Filling the information gaps Prolific data on financial institutions can ensure better monitoring. T K Arun A brain graft for the ruling alliance That the UPA needs the services of an advisory council is testimony to the bankruptcy of politics. Swaminathan S Anklesaria Aiyar Shale gas transforms geopolitics, energy For decades, India has kowtowed to Gulf countries, notably Iran. With large shale gas deposits and new technology to extract it, India can afford to act tough, says Swaminathan S Anklesaria Aiyar. |
India's Debt Situation
India's debt situation focuses on the total amount of external debts taken by the nation in a particular year, its repayments as well as the outstanding debt amounts, if any.
India's External Debt Situation: 2009
India's external debt, as of March 2009, was US$229.9 billion (22.0 % of GDP), recording an increase of US$5.3 billion or 2.4 % over 2008 mainly due to the increase in trade credits. According to an international comparison of external debt of the twenty most indebted countries, India was the fifth most indebted country in 2007. By way of composition of external debt, the share of commercial borrowings was the highest at 27.3% in March 2009, followed by short-term debt (21.5%), NRI deposits (18.1%t) and multilateral debt (17.%).
The debt service ratio has declined steadily over the years, standing at 4.6% in March 2009. By not taking into account the effects of the appreciation of the US dollar against other major currencies and the Indian rupee, the stock of external debt would have increased by US$18.7 billion, as compared to the stock in March 2008. The share of short-term debt in the total debt increased to 21.5% in March 2009, from 20.9% in March 2008, primarily on account of a rise in short-term trade credits.
Based on residual maturity, the short-term debt accounted for 40.6% of the total external debt on March 2009. The ratio of short-term debt to foreign exchange reserves stood at 19.6% in March 2009, higher than the 15.2% in March 2008. The US dollar continued as the dominant currency, accounting for 57.1% of the total external debt stock in March 2009. India's foreign exchange reserves provided a cover of 109.6% to the external debt stock at the end of March 2009, as compared to 137.9% at the end of March 2008.
Indian Debt Rating and 2010 Outlook
India's credit rating outlook was raised to 'stable' from 'negative' by Standard & Poor's based on optimism that faster growth in Asia's third-largest economy will help the government cut its budget deficit. The Indian Finance Minister has promised to cut the deficit to 5.5% of the GDP in 2010, from 6.9% of the GDP in 2009. The government also plans to cut its debt to 68% of the GDP by 2015, from its current levels of 80%.
Related Links
- India and the Global Economy
- World Bank Lending To India's Health Sector
- NRI Deposits: Indiam NRI Accounts and Interest Rates
- Indian Insurance Policies
- Indian Pensions: Varishtha Pension Bima Yojana
- India's Universal Health Insurance Scheme
- Indian Insurance Companies
- Indian Economy 2006 - 2007 (India Economy 06-07)
- Indian Economy in 2005 - 2006 (India Economy 05-06)
- The Indian Insurance Industry
- India Economic Summit (Dec 5-7, 2004, New Delhi, India)
- India Economic Reform: After Congress Landslide Victory, Real Reform Likely
- General Insurance Corporation of India
- CAC (Capital Account Convertibility) in the Indian Economy
- Agriculture Insurance In India
- Poverty in India
- India Fiscal Sector Reforms
- India Current Account Deficit
- Indian External Sector
- Indian Economy Statistics
- Indian Economy Overview
- Indian Economic Structure: Indian Industry Sectors & Industries
- Indian Economic Reforms
- India Economic Development
- Indian Trade with the World
- Indian Economy Overview
- Indian Economic Indicators
- India's Trade, Exports and Imports
- India at a Glance
- Indian Inflation
- Indian National Income Consumption Expenditure, Saving And Capital Formation, 2004 to 2005
- Indian Macroeconomic And Monetary Developments in 2004-2005
- Indian Millennium Development Goals (MDGS) - India Country Report
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks In India Addressed At Indo-German Business Summit
- India's Foreign Trade Data (For April-June, 2006-2007)
- Advance Estimates Of Indian National Income, 2005-06
- What is the Economic Effect of the Flooding in Bihar?
Economy of India
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Economy of The Republic of India | |
|---|---|
 Modern Indian notes | |
| Rank | 11th |
| Currency | 1 Indian Rupee (INR) (₨) = 100 Paise |
| Fiscal year | 1 April — 31 March |
| Trade organizations | WTO, SAFTA, G-20 and others |
| Statistics | |
| GDP | $1.236 trillion (2009)[1] (nominal; 11th) $3.526 trillion (2009)[1] (PPP; 4th) |
| GDP growth | 7.4% (2009/2010)[2] |
| GDP per capita | $1,030 (2009)[1] (nominal; 139th) $2,940 (2009)[1] (PPP; 128th) |
| GDP by sector | agriculture (17.5%), industry (20%), services (62.5%) (2009 est.) |
| Inflation (CPI) | 10.16% (May. 2010)[3] Food inflation (16.87%) (Apr. 2010)[3] |
| Population below poverty line | 37.2% (2010)[4] 410 million (2010)[4] |
| Gini index | 36.8 (List of countries) |
| Labour force | 467 million (2009 est.) (2nd) |
| Labour force by occupation | agriculture (52%), industry (14%), services (34%) (2003) |
| Unemployment | 9.5% (2009 est.)[5] |
| Main industries | telecommunications, textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, information technology |
| External | |
| Exports | $155 billion f.o.b (2009 est.) |
| Export goods | software, petroleum products, textile goods, gems and jewelry, engineering goods, chemicals, leather manufactures |
| Main export partners | US 12.3%, UAE 9.4%, China 9.3% (2008) |
| Imports | $232.3 billion f.o.b (2009 est.) |
| Import goods | crude oil, machinery, gems, fertilizer, chemicals |
| Main import partners | China 11.1%, Saudi Arabia 7.5%, US 6.6%, UAE 5.1%, Iran 4.2%, Singapore 4.2%, Germany 4.2% (2008) |
| FDI stock | $156.30 billion (31 December 2009 est.) |
| Gross external debt | $232.5 billion (31 December 2009 est.)[6] |
| Public finances | |
| Public debt | $163.8 billion (2009)[7] 60.1% of GDP |
| Revenues | $153.5 billion (2008 est.) |
| Expenses | $223 billion (2009 est.) |
| Economic aid | $1.724 billion (2005)[8] |
| Foreign reserves | $287.37 billion (end-Dec 2009) (5th) |
| Main data source: CIA World Fact Book All values, unless otherwise stated, are in US dollars | |
The economy of India is the eleventh largest economy in the world by nominal GDP[1] and the fourth largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).[9] In the 1990s, following economic reform from the socialist-inspired economy of post-independence India, the country began to experience rapid economic growth, as markets opened for international competition and investment. In the 21st century, India is an emerging economic power with vast human and natural resources, and a huge knowledge base. Economists predict that by 2020,[10] India will be among the leading economies of the world.
India was under social democratic-based policies from 1947 to 1991. The economy was characterised by extensive regulation, protectionism, public ownership, pervasive corruption and slow growth.[11][12][13][14] Since 1991, continuing economic liberalisation has moved the economy towards a market-based system.[12][13] A revival of economic reforms and better economic policy in 2000s accelerated India's economic growth rate. In recent years, Indian cities have continued to liberalize business regulations.[15] By 2008, India had established itself as the world's second-fastest growing major economy.[16][17][18] However, the year 2009 saw a significant slowdown in India's official GDP growth rate to 6.1%[19] as well as the return of a large projected fiscal deficit of 6.8% of GDP which would be among the highest in the world.[20][21]
India's large service industry accounts for 62.5% of the country's GDP while the industrial and agricultural sector contribute 20% and 17.5% respectively. Agriculture is the predominant occupation in India, accounting for about 52% of employment. The service sector makes up a further 34%, and industrial sector around 14%.[22] The labor force totals half a billion workers. Major agricultural products include rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes, cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry and fish.[23] Major industries include telecommunications, textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, information technology enabled services and software.[23]
India's per capita income (nominal) is $1,030, ranked 139th in the world,[24] while its per capita (PPP) of US$2,940 is ranked 128th.[25][26] Previously a closed economy, India's trade has grown fast.[12] India currently accounts for 1.5% of World trade as of 2007 according to the WTO. According to the World Trade Statistics of the WTO in 2006, India's total merchandise trade (counting exports and imports) was valued at $294 billion in 2006 and India's services trade inclusive of export and import was $143 billion. Thus, India's global economic engagement in 2006 covering both merchandise and services trade was of the order of $437 billion, up by a record 72% from a level of $253 billion in 2004. India's trade has reached a still relatively moderate share 24% of GDP in 2006, up from 6% in 1985.[12]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] History

India's economic history can be broadly divided into three eras, beginning with the pre-colonial period lasting up to the 18th century. The advent of British colonisation started the colonial period in the early 19th century, which ended with independence in 1947. The third period stretches from independence in 1947 until now.
[edit] Pre-colonial
The citizens of the Indus Valley civilisation, a permanent settlement that flourished between 2800 BC and 1800 BC, practiced agriculture, domesticated animals, used uniform weights and measures, made tools and weapons, and traded with other cities. Evidence of well planned streets, a drainage system and water supply reveals their knowledge of urban planning, which included the world's first urban sanitation systems and the existence of a form of municipal government.[29]
The 1872 census revealed that 99.3% of the population of the region constituting present-day India resided in villages,[30] whose economies were largely isolated and self-sustaining, with agriculture the predominant occupation. This satisfied the food requirements of the village and provided raw materials for hand-based industries, such as textiles, food processing and crafts. Although many kingdoms and rulers issued coins, barter was prevalent. Villages paid a portion of their agricultural produce as revenue to the rulers, while its craftsmen received a part of the crops at harvest time for their services.[31]
Religion, especially Hinduism, and the caste and the joint family systems, played an influential role in shaping economic activities.[32] The caste system functioned much like medieval European guilds, ensuring the division of labour, providing for the training of apprentices and, in some cases, allowing manufacturers to achieve narrow specialization. For instance, in certain regions, producing each variety of cloth was the specialty of a particular sub-caste.

Textiles such as muslin, Calicos, shawls, and agricultural products such as pepper, cinnamon, opium and indigo were exported to Europe, the Middle East and South East Asia in return for gold and silver.[34]
Assessment of India's pre-colonial economy is mostly qualitative, owing to the lack of quantitative information. One estimate puts the revenue of Akbar's Mughal Empire in 1600 at £17.5 million, in contrast with the total revenue of Great Britain in 1800, which totalled £16 million.[35] India, by the time of the arrival of the British, was a largely traditional agrarian economy with a dominant subsistence sector dependent on primitive technology. It existed alongside a competitively developed network of commerce, manufacturing and credit. After the decline of the Mughals, western, central and parts of south and north India were integrated and administered by the Maratha Empire. The Maratha Empire's budget in 1740s, at its peak, was Rs. 100 million. After the loss at Panipat, the Maratha Empire disintegrated into confederate states of Gwalior, Baroda, Indore, Jhansi, Nagpur, Pune and Kolhapur. Gwalior state had a budget of Rs. 30M. However, at this time, British East India company entered the Indian political theatre. Until 1857, when India was firmly under the British crown, the country remained in a state of political instability due to internecine wars and conflicts.[36]
[edit] Colonial

Company rule in India brought a major change in the taxation environment from revenue taxes to property taxes, resulting in mass impoverishment and destitution of majority of farmers and led to numerous famines.[37] The economic policies of the British Raj effectively bankrupted India's large handicrafts industry and caused a massive drain of India's resources.[38][39] Indian Nationalists employed the successful Swadeshi movement, as strategy to diminish British economic superiority by boycotting British products and the reviving the market for domestic-made products and production techniques. India had become a strong market for superior finished European goods. This was because of vast gains made by the Industrial revolution in Europe, the effects of which was deprived to Colonial India.
The Nationalists had hoped to revive the domestic industries that were badly effected by polices implemented by British Raj which had made them uncompetitive to British made goods.
An estimate by Cambridge University historian Angus Maddison reveals that "India's share of the world income fell from 22.6% in 1700, comparable to Europe's share of 23.3%, to a low of 3.8% in 1952".[40] It also created an institutional environment that, on paper, guaranteed property rights among the colonizers, encouraged free trade, and created a single currency with fixed exchange rates, standardized weights and measures, capital markets. It also established a well developed system of railways and telegraphs, a civil service that aimed to be free from political interference, a common-law and an adversarial legal system.[41] India's colonisation by the British coincided with major changes in the world economy—industrialisation, and significant growth in production and trade. However, at the end of colonial rule, India inherited an economy that was one of the poorest in the developing world,[42] with industrial development stalled, agriculture unable to feed a rapidly growing population, India had one of the world's lowest life expectancies, and low rates for literacy.
The impact of the British rule on India's economy is a controversial topic. Leaders of the Indian independence movement, and left-nationalist economic historians have blamed colonial rule for the dismal state of India's economy in its aftermath and that financial strength required for Industrial development in Europe was derived from the wealth taken from Colonies in Asia and Africa. At the same time right-wing historians have countered that India's low economic performance was due to various sectors being in a state of growth and decline due to changes brought in by colonialism and a world that was moving towards industrialization and economic integration.[43]
[edit] Independence to 1991

Indian economic policy after independence was influenced by the colonial experience (which was seen by Indian leaders as exploitative in nature) and by those leaders' exposure to Fabian socialism. Policy tended towards protectionism, with a strong emphasis on import substitution, industrialization, state intervention in labor and financial markets, a large public sector, business regulation, and central planning.[44] Five-Year Plans of India resembled central planning in the Soviet Union. Steel, mining, machine tools, water, telecommunications, insurance, and electrical plants, among other industries, were effectively nationalized in the mid-1950s.[45] Elaborate licences, regulations and the accompanying red tape, commonly referred to as Licence Raj, were required to set up business in India between 1947 and 1990.[46]
Jawaharlal Nehru, the first prime minister, along with the statistician Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis, carried on by Indira Gandhi formulated and oversaw economic policy. They expected favorable outcomes from this strategy, because it involved both public and private sectors and was based on direct and indirect state intervention, rather than the more extreme Soviet-style central command system.[47][dead link] The policy of concentrating simultaneously on capital- and technology-intensive heavy industry and subsidizing manual, low-skill cottage industries was criticized by economist Milton Friedman, who thought it would waste capital and labour, and retard the development of small manufacturers.[48][dead link] The rate from 1947–80 was derisively referred to as the Hindu rate of growth, because of the unfavourable comparison with growth rates in other Asian countries, especially the "East Asian Tigers".[41]
The Rockefeller Foundation's research in high-yielding varieties of seeds, their introduction after 1965 and the increased use of fertilizers and irrigation are known collectively as the Green Revolution in India, which provided the increase in production needed to make India self-sufficient in food grains, thus improving agriculture in India. Famine in India, once accepted as inevitable, has not returned since independence.
[edit] Since 1991

In the late 80s, the government led by Rajiv Gandhi eased restrictions on capacity expansion for incumbents, removed price controls and reduced corporate taxes. While this increased the rate of growth, it also led to high fiscal deficits and a worsening current account. The collapse of the Soviet Union, which was India's major trading partner, and the first Gulf War, which caused a spike in oil prices, caused a major balance-of-payments crisis for India, which found itself facing the prospect of defaulting on its loans.[50] India asked for a $1.8 billion bailout loan from IMF, which in return demanded reforms.[51]
In response, Prime Minister Narasimha Rao along with his finance minister Dr. Manmohan Singh initiated the economic liberalisation of 1991. The reforms did away with the Licence Raj (investment, industrial and import licensing) and ended many public monopolies, allowing automatic approval of foreign direct investment in many sectors.[52] Since then, the overall direction of liberalisation has remained the same, irrespective of the ruling party, although no party has tried to take on powerful lobbies such as the trade unions and farmers, or contentious issues such as reforming labour laws and reducing agricultural subsidies.[53] Since 1990 India has emerged as one of the fastest-growing economies in the developing world; during this period, the economy has grown constantly, but with a few major setbacks. This has been accompanied by increases in life expectancy, literacy rates and food security.
While the credit rating of India was hit by its nuclear tests in 1998, it has been raised to investment level in 2007 by S&P and Moody's.[54] In 2003, Goldman Sachs predicted that India's GDP in current prices will overtake France and Italy by 2020, Germany, UK and Russia by 2025 and Japan by 2035. By 2035, it was projected to be the third largest economy of the world, behind US and China. India is often seen by most economists as a rising economic superpower and is believed to play a major role in the global economy in the 21st century.[55][56] In 2009 India purchased 200 Tons of Gold for $6.7 billion from IMF[57] as a total role reversal from 1991.
[edit] Sectors
[edit] Industry and services


Industry accounts for 54.6% of the GDP and employ 17% of the total workforce.[22] However, about one-third of the industrial labour force is engaged in simple household manufacturing only.[63][dead link] In absolute terms, India is 16th in the world in terms of nominal factory output.[64].
Economic reforms brought foreign competition, led to privatisation of certain public sector industries, opened up sectors hitherto reserved for the public sector and led to an expansion in the production of fast-moving consumer goods.[65] Post-liberalisation, the Indian private sector, which was usually run by oligopolies of old family firms and required political connections to prosper was faced with foreign competition, including the threat of cheaper Chinese imports. It has since handled the change by squeezing costs, revamping management, focusing on designing new products and relying on low labour costs and technology.[66]
Textile manufacturing is the second largest source for employment after agriculture and accounts for 26% of manufacturing output.[67] Ludhiana produces 90% of woolens in India and is also Known as the Manchester of India. Tirupur has gained universal recognition as the leading source of hosiery, knitted garments, casual wear and sportswear.[68] Dharavi slum in Mumbai has gained fame for leather products. Tata Motors' Nano attempts to be the world's cheapest car.[62]
India is fifteenth in services output. It provides employment to 23% of work force, and it is growing fast, growth rate 7.5% in 1991–2000 up from 4.5% in 1951–80. It has the largest share in the GDP, accounting for 55% in 2007 up from 15% in 1950.[22]
Business services (information technology, information technology enabled services, business process outsourcing) are among the fastest growing sectors contributing to one third of the total output of services in 2000. The growth in the IT sector is attributed to increased specialization, and an availability of a large pool of low cost, but highly skilled, educated and fluent English-speaking workers, on the supply side, matched on the demand side by an increased demand from foreign consumers interested in India's service exports, or those looking to outsource their operations. The share of India's IT industry to the country's GDP increased from 4.8 % in 2005-06 to 7% in 2008.[69][70] In 2009, seven Indian firms were listed among the top 15 technology outsourcing companies in the world.[71] In March 2009, annual revenues from outsourcing operations in India amounted to US$60 billion and this is expected to increase to US$225 billion by 2020.[72]
Organized retail such supermarkets accounts for 24% of the market as of 2008.[73] Regulations prevent most foreign investment in retailing. Moreover, over thirty regulations such as "signboard licences" and "anti-hoarding measures" may have to be complied before a store can open doors. There are taxes for moving goods to states, from states, and even within states.[73]
Tourism in India is relatively undeveloped, but growing at double digits. Some hospitals woo medical tourism.[74]
[edit] Agriculture

India ranks second worldwide in farm output. Agriculture and allied sectors like forestry, logging and fishing accounted for 16.6% of the GDP in 2007, employed 60% of the total workforce[22] and despite a steady decline of its share in the GDP, is still the largest economic sector and plays a significant role in the overall socio-economic development of India. Yields per unit area of all crops have grown since 1950, due to the special emphasis placed on agriculture in the five-year plans and steady improvements in irrigation, technology, application of modern agricultural practices and provision of agricultural credit and subsidies since Green revolution in India. However, international comparisons reveal the average yield in India is generally 30% to 50% of the highest average yield in the world.[77]
India is the largest producer in the world of milk, cashew nuts, coconuts, tea, ginger, turmeric and black pepper.[78] It also has the world's largest cattle population: 193 million.[79] It is the second largest producer of wheat, rice, sugar, cotton, silk, peanuts and inland fish.[80] It is the third largest producer of tobacco.[80] India is the largest fruit producer, accounting for 10% of the world fruit production. It is the leading producer of bananas, sapotas and mangoes.[80]
India is the second largest producer and the largest consumer of silk in the world, with the majority of the 77 million kg (2005)[81] production taking place in Karnataka State, particularly in Mysore and the North Bangalore regions of Muddenahalli, Kanivenarayanapura, and Doddaballapura, the upcoming sites of a INR 700 million "Silk City".[82][83]
[edit] Banking and finance
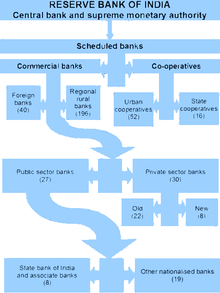
The Indian money market is classified into: the organised sector (comprising private, public and foreign owned commercial banks and cooperative banks, together known as scheduled banks); and the unorganised sector (comprising individual or family owned indigenous bankers or money lenders and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs)). The unorganised sector and microcredit are still preferred over traditional banks in rural and sub-urban areas, especially for non-productive purposes, like ceremonies and short duration loans.[85]
Prime Minister Indira Gandhi nationalised 14 banks in 1969, followed by six others in 1980, and made it mandatory for banks to provide 40% of their net credit to priority sectors like agriculture, small-scale industry, retail trade, small businesses, etc. to ensure that the banks fulfill their social and developmental goals. Since then, the number of bank branches has increased from 10,120 in 1969 to 98,910 in 2003 and the population covered by a branch decreased from 63,800 to 15,000 during the same period. The total deposits increased 32.6 times between 1971 to 1991 compared to 7 times between 1951 to 1971. Despite an increase of rural branches, from 1,860 or 22% of the total number of branches in 1969 to 32,270 or 48%, only 32,270 out of 5 lakh (500,000) villages are covered by a scheduled bank.[86][87]
The public sector banks hold over 75% of total assets of the banking industry, with the private and foreign banks holding 18.2% and 6.5% respectively.[88] Since liberalisation, the government has approved significant banking reforms. While some of these relate to nationalised banks (like encouraging mergers, reducing government interference and increasing profitability and competitiveness), other reforms have opened up the banking and insurance sectors to private and foreign players.[22][89]
More than half of personal savings are invested in physical assets such as land, houses, cattle, and gold.[90]
[edit] Natural resources

India's total cultivable area is 1,269,219 km² (56.78% of total land area), which is decreasing due to constant pressure from an ever growing population and increased urbanisation. India has a total water surface area of 314,400 km² and receives an average annual rainfall of 1,100 mm. Irrigation accounts for 92% of the water utilisation, and comprised 380 km² in 1974, and is expected to rise to 1,050 km² by 2025, with the balance accounted for by industrial and domestic consumers. India's inland water resources comprising rivers, canals, ponds and lakes and marine resources comprising the east and west coasts of the Indian ocean and other gulfs and bays provide employment to nearly 6 million people in the fisheries sector. In 2008, India had the world's third largest fishing industry.[91]
India's major mineral resources include coal, iron, manganese, mica, bauxite, titanium, chromite, limestone and thorium. India meets most of its domestic energy demand through its 92 billion tonnes of coal reserves (about 10% of world's coal reserves).[92]
India's huge thorium reserves — about 25% of world's reserves — is expected to fuel the country's ambitious nuclear energy program in the long-run. India's dwindling uranium reserves stagnated the growth of nuclear energy in the country for many years.[93] However, the Indo-US nuclear deal has paved the way for India to import uranium from other countries.[94] India is also believed to be rich in certain renewable sources of energy with significant future potential such as solar, wind and biofuels (jatropha, sugarcane).
[edit] Petroleum and Natural gas

India's oil reserves, found in Bombay High, parts of Gujarat, Rajasthan and eastern Assam, meet 25% of the country's domestic oil demand.[22][96] India's total proven oil reserves stand at 11 billion barrels,[97] of which Bombay High is believed to hold 6.1 billion barrels[98] and Mangala Area in Rajasthan an additional 3.6 billion barrels.[99]
In 2009, India imported 2.56 million barrels of oil per day, making it one of largest buyers of crude oil in the world.[100] The petroleum industry in India mostly consists of public sector companies such as Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) and Indian Petrochemicals Corporation Limited (IPCL). There are some major private Indian companies in oil sector such as Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) which operates the world's largest oil refining complex.[101]
[edit] Pharmaceuticals
India has a self reliant Pharmaceuticals industry. The majority of its medical consumables are produced domestically. Pharmaceutical Industry in India is dotted with companies like Ranbaxy Laboratories, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, Cipla which have created a niche for themselves at world level.
Today, India is an exporter to countries like the United States and Russia. In terms of the global market, India currently holds a modest 1-2% share, but it has been growing at approximately 10% per year. Indian Pharmaceutical Industry is often compared to Pharmaceutical Industry in the USA.
[edit] External trade and investment
[edit] Global trade relations

India's economy is mostly dependent on its large internal market with external trade accounting for just 20% of the country's GDP.[103] In 2008, India accounted for 1.45% of global merchandise trade and 2.8% of global commercial services export.[104] Until the liberalization of 1991, India was largely and intentionally isolated from the world markets, to protect its economy and to achieve self-reliance. Foreign trade was subject to import tariffs, export taxes and quantitative restrictions, while foreign direct investment (FDI) was restricted by upper-limit equity participation, restrictions on technology transfer, export obligations and government approvals; these approvals were needed for nearly 60% of new FDI in the industrial sector. The restrictions ensured that FDI averaged only around US$200 million annually between 1985 and 1991; a large percentage of the capital flows consisted of foreign aid, commercial borrowing and deposits of non-resident Indians.[105] India's exports were stagnant for the first 15 years after independence, due to the predominance of tea, jute and cotton manufactures, demand for which was generally inelastic. Imports in the same period consisted predominantly of machinery, equipment and raw materials, due to nascent industrialization.
Since liberalization, the value of India's international trade has become more broad-based and has risen to Rs. 63,080,109 crores in 2003–04 from Rs.1,250 crores in 1950–51. India's major trading partners are China, the US, the UAE, the UK, Japan and the EU.[106] The exports during April 2007 were $12.31 billion up by 16% and import were $17.68 billion with an increase of 18.06% over the previous year.[107] In 2006-07, major export commodities included engineering goods, petroleum products, chemicals and pharmaceuticals, gems and jewellery, textiles and garments, agricultural products, iron ore and other minerals. Major import commodities included crude oil and related products, machinery, electronic goods, gold and silver.[108]
India is a founding-member of General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) since 1947 and its successor, the WTO. While participating actively in its general council meetings, India has been crucial in voicing the concerns of the developing world. For instance, India has continued its opposition to the inclusion of such matters as labour and environment issues and other non-tariff barriers into the WTO policies.[109]
[edit] Balance of payments
Since independence, India's balance of payments on its current account has been negative. Since liberalisation in the 1990s (precipitated by a balance of payment crisis), India's exports have been consistently rising, covering 80.3% of its imports in 2002–03, up from 66.2% in 1990–91. India's growing oil import bill is seen as the main driver behind the large current account deficit.[110] In 2007-08, India imported 120.1 million tonnes of crude oil, more than 3/4th of the domestic demand, at a cost of $61.72 billion.[111]
Although India is still a net importer, since 1996–97 its overall balance of payments (i.e., including the capital account balance) has been positive, largely on account of increased foreign direct investment and deposits from non-resident Indians; until this time, the overall balance was only occasionally positive on account of external assistance and commercial borrowings. As a result, India's foreign currency reserves stood at $285 billion in 2008.
Due to the global late-2000s recession, both Indian exports and imports declined by 29.2% and 39.2% respectively in June 2009.[112] The steep decline was because countries hit hardest by the global recession, such as United States and members of the European Union, account for more than 60% of Indian exports.[113] However, since the decline in imports was much sharper compared to the decline in exports, India's trade deficit reduced to 252.5 billion rupee.[112]
India's reliance on external assistance and commercial borrowings has decreased since 1991–92, and since 2002–03, it has gradually been repaying these debts. Declining interest rates and reduced borrowings decreased India's debt service ratio to 4.5% in 2007.[114] ‹See Tfd› In India, External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) are being permitted by the Government for providing an additional source of funds to Indian corporates. The Ministry of Finance monitors and regulates these borrowings (ECBs) through ECB policy guidelines.[115]
[edit] Foreign direct investment in India
Share of top five investing countries in FDI inflows. (2000–2007)[116]| Rank | Country | Inflows (Million USD) | Inflows (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85,178 | 44.24%[117] | |
| 2 | 18,040 | 9.37% | |
| 3 | 15,363 | 7.98% | |
| 4 | 11,177 | 5.81% | |
| 5 | 9,742 | 5.06% | |
| 6 | 5,742 | 3.06% |
As the fourth-largest economy in the world in PPP terms, India is a preferred destination for foreign direct investments (FDI);[118] India has strengths in telecommunication, information technology and other significant areas such as auto components, chemicals, apparels, pharmaceuticals, and jewellery. Despite a surge in foreign investments, rigid FDI policies resulted in a significant hindrance. However, due to some positive economic reforms aimed at deregulating the economy and stimulating foreign investment, India has positioned itself as one of the front-runners of the rapidly growing Asia Pacific Region.[118] India has a large pool of skilled managerial and technical expertise. The size of the middle-class population stands at 300 million and represents a growing consumer market.[119]
The inordinately high investment from Mauritius is due to routing of international funds through the country given significant capital gains tax advantages; double taxation is avoided due to a tax treaty between India and Mauritius, and Mauriitus is a capital gains tax haven, effectively creating a zero-taxation FDI channel.
India's recently liberalized FDI policy (2005) allows up to a 100% FDI stake in ventures. Industrial policy reforms have substantially reduced industrial licensing requirements, removed restrictions on expansion and facilitated easy access to foreign technology and foreign direct investment FDI. The upward moving growth curve of the real-estate sector owes some credit to a booming economy and liberalized FDI regime. In March 2005, the government amended the rules to allow 100 per cent FDI in the construction business.[120] This automatic route has been permitted in townships, housing, built-up infrastructure and construction development projects including housing, commercial premises, hotels, resorts, hospitals, educational institutions, recreational facilities, and city- and regional-level infrastructure.
A number of changes were approved on the FDI policy to remove the caps in most sectors. Fields which require relaxation in FDI restrictions include civil aviation, construction development, industrial parks, petroleum and natural gas, commodity exchanges, credit-information services and mining. But this still leaves an unfinished agenda of permitting greater foreign investment in politically sensitive areas such as insurance and retailing. FDI inflows into India reached a record $19.5 billion in fiscal year 2006-07 (April-March), according to the government's Secretariat for Industrial Assistance. This was more than double the total of US$7.8bn in the previous fiscal year. The FDI inflow for 2007-08 has been reported as $24 billion[121] and for 2008-09, it is expected to be above $35 billion.[122] A critical factor in determining India's continued economic growth and realizing the potential to be an economic superpower is going to depend on how the government can create incentives for FDI flow across a large number of sectors in India.[123]
[edit] Currency
The Indian rupee is the only legal tender accepted in India. The exchange rate as on 23 March 2010 is 45.40 INR the USD,[124] 61.45 to a EUR, and 68.19 to a GBP. The Indian rupee is accepted as legal tender in the neighboring Nepal and Bhutan, both of which peg their currency to that of the Indian rupee. The rupee is divided into 100 paise. The highest-denomination banknote is the 1,000 rupee note; the lowest-denomination coin in circulation is the 25 paise coin (it earlier had 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20 paise coins which have been discontinued by the Reserve Bank of India).[125]
The Rupee hit a record low during early 2009 on account of global recession. However, due to a strong domestic market, India managed to bounce back sooner than the western countries. Since September 2009 there has been a constant appreciation in Rupee versus most Tier 1 currencies. On 11 January 2010 Rupee went as high as 45.50 to a United states dollar and on 10 January 2010 as high as Rupee 73.93 to a British Pound. A rising rupee also prompted Government of India to buy 200 tonnes of Gold from IMF.
The RBI, the country's central bank was established on 1 April 1935. It serves as the nation's monetary authority, regulator and supervisor of the financial system, manager of exchange control and as an issuer of currency. The RBI is governed by a central board, headed by a governor who is appointed by the Central government of India.
[edit] Income and consumption
As of 2005:
- 85.7% of the population lives on less than $2.50 (PPP) a day, down from 92.5% in 1981. This is much higher than the 80.5% in Sub-Saharan Africa.[126]
- 75.6% of the population lives on less than $2 a day (PPP), which is around 20 rupees or $0.5 a day in nominal terms. It was down from 86.6%, but is still even more than the 73.0% in Sub-Saharan Africa.[126][127][128][129][130]
- 24.3% of the population earned less than $1 (PPP, around $0.25 in nominal terms) a day in 2005, down from 42.1% in 1981.[126][131]
- 41.6% of its population is living below the new international poverty line of $1.25 (PPP) per day, down from 59.8% in 1981.[126] The World Bank further estimates that a third of the global poor now reside in India.
Today, more people can afford a bicycle than ever before. Some 40% of Indian households owns a bicycle, with ownership rates ranging from around 30% to 70% at state level.[132] Housing is modest. According to Times of India, "a majority of Indians have per capita space equivalent to or less than a 10 feet x 10 feet room for their living, sleeping, cooking, washing and toilet needs." and "one in every three urban Indians lives in homes too cramped to exceed even the minimum requirements of a prison cell in the US."[133] The average is 103 sq ft (9.6 m2) per person in rural areas and 117 sq ft (10.9 m2) per person in urban areas.[133]
Around half of Indian children are malnourished. The proportion of underweight children is nearly double that of Sub-Saharan Africa.[134][135] However, India has not had famines since the Green Revolution in the early 1970s. While poverty in India has reduced significantly, official figures estimate that 27.5%[136] of Indians still lived below the national poverty line of $1 (PPP, around 10 rupees in nominal terms) a day in 2004-2005.[137] A 2007 report by the state-run National Commission for Enterprises in the Unorganised Sector (NCEUS) found that 65% of Indians, or 750 million people, lived on less than 20 rupees per day[138] with most working in "informal labour sector with no job or social security, living in abject poverty."[139]
Since the early 1950s, successive governments have implemented various schemes, under planning, to alleviate poverty, that have met with partial success. All these programmes have relied upon the strategies of the Food for work programme and National Rural Employment Programme of the 1980s, which attempted to use the unemployed to generate productive assets and build rural infrastructure.[140] In August 2005, the Indian parliament passed the Rural Employment Guarantee Bill, the largest programme of this type in terms of cost and coverage, which promises 100 days of minimum wage employment to every rural household in all the India's 600 districts. ‹See Tfd› The question of whether economic reforms have reduced poverty or not has fuelled debates without generating any clear cut answers and has also put political pressure on further economic reforms, especially those involving the downsizing of labour and cutting agricultural subsidies.[141][142]
[edit] Employment
Agricultural and allied sectors accounted for about 60% of the total workforce in 2003 same as in 1993–94. While agriculture has faced stagnation in growth, services have seen a steady growth. Of the total workforce, 8% is in the organised sector, two-thirds of which are in the public sector. The NSSO survey estimated that in 1999–2000, 106 million, nearly 10% of the population were unemployed and the overall unemployment rate was 7.3%, with rural areas doing marginally better (7.2%) than urban areas (7.7%). India's labor force is growing by 2.5% annually, but employment only at 2.3% a year.[143]
Official unemployment exceeds 9%. Regulation and other obstacles have discouraged the emergence of formal businesses and jobs. Almost 30% of workers are casual workers who work only when they are able to get jobs and remain unpaid for the rest of the time.[143] Only 10% of the workforce is in regular employment.[143] India's labor regulations are heavy even by developing country standards and analysts have urged the government to abolish them.[12][144]
Unemployment in India is characterized by chronic or disguised unemployment. Government schemes that target eradication of both poverty and unemployment (which in recent decades has sent millions of poor and unskilled people into urban areas in search of livelihoods) attempt to solve the problem, by providing financial assistance for setting up businesses, skill honing, setting up public sector enterprises, reservations in governments, etc. The decreased role of the public sector after liberalization has further underlined the need for focusing on better education and has also put political pressure on further reforms.[140][145]
Child labor is a complex problem that is basically rooted in poverty. The Indian government is implementing the world's largest child labor elimination program, with primary education targeted for ~250 million. Numerous non-governmental and voluntary organizations are also involved. Special investigation cells have been set up in states to enforce existing laws banning employment of children (under 14) in hazardous industries. The allocation of the Government of India for the eradication of child labor was $10 million in 1995-96 and $16 million in 1996-97. The allocation for 2007 is $21 million.[146]
In 2006, remittances from Indian migrants overseas made up $27 billion or about 3% of India's GDP.[147]
[edit] Economic trends
In the revised 2007 figures, based on increased and sustaining growth, more inflows into foreign direct investment, Goldman Sachs predicts that "from 2007 to 2020, India's GDP per capita in US$ terms will quadruple", and that the Indian economy will surpass the United States (in US$) by 2043.[14] In spite of the high growth rate, the report stated that India would continue to remain a low-income country for decades to come but could be a "motor for the world economy" if it fulfills its growth potential.[14] Goldman Sachs has outlined 10 things that it needs to do in order to achieve its potential and grow 40 times by 2050. These are
- improve governance
- raise educational achievement
- increase quality and quantity of universities
- control inflation
- introduce a credible fiscal policy
- liberalize financial markets
- increase trade with neighbours
- increase agricultural productivity
- improve infrastructure and
- improve environmental quality.[149]
[edit] Issues
[edit] Agriculture
Slow agricultural growth is a concern for policymakers as some two-thirds of India's people depend on rural employment for a living. Current agricultural practices are neither economically nor environmentally sustainable and India's yields for many agricultural commodities are low. Poorly maintained irrigation systems and almost universal lack of good extension services are among the factors responsible. Farmers' access to markets is hampered by poor roads, rudimentary market infrastructure, and excessive regulation.
– World Bank: "India Country Overview 2008"[150]
The low productivity in India is a result of the following factors:
- According to "India: Priorities for Agriculture and Rural Development" by World Bank, India's large agricultural subsidies are hampering productivity-enhancing investment. Overregulation of agriculture has increased costs, price risks and uncertainty. Government interventions in labor, land, and credit markets are hurting the market. Infrastructure and services are inadequate.[151]
- Illiteracy, slow progress in implementing land reforms and inadequate or inefficient finance and marketing services for farm produce.
- The average size of land holdings is very small (less than 20,000 m²) and is subject to fragmentation, due to land ceiling acts and in some cases, family disputes. Such small holdings are often over-manned, resulting in disguised unemployment and low productivity of labour.
- Adoption of modern agricultural practices and use of technology is inadequate, hampered by ignorance of such practices, high costs and impracticality in the case of small land holdings.
- World Bank says that the allocation of water is inefficient, unsustainable and inequitable. The irrigation infrastructure is deteriorating.[151] Irrigation facilities are inadequate, as revealed by the fact that only 52.6% of the land was irrigated in 2003–04,[152] which result in farmers still being dependent on rainfall, specifically the Monsoon season. A good monsoon results in a robust growth for the economy as a whole, while a poor monsoon leads to a sluggish growth.[153] Farm credit is regulated by NABARD, which is the statutory apex agent for rural development in the subcontinent.
India has many farm insurance companies that insure wheat, fruit, rice and rubber farmers in the event of natural disasters or catastrophic crop failure, under the supervision of the Ministry of Agriculture. One notable company that provides all of these insurance policies is Agriculture Insurance Company of India and it alone insures almost 20 million farmers.
India's population is growing faster than its ability to produce rice and wheat.[154] The most important structural reform for self-sufficiency is the ITC Limited plan to connect 20,000 villages to the Internet by 2013.[155] This will provide farmers with up to date crop prices for the first time, which should minimise losses incurred from neighbouring producers selling early and in turn facilitate investment in rural areas.
[edit] Corruption
Corruption has been one of the pervasive problems affecting India. The economic reforms of 1991 reduced the red tape, bureaucracy and the Licence Raj that had strangled private enterprise and was blamed by Chakravarthi Rajagopalachari for the corruption and inefficiencies. Yet, a 2005 study by Transparency International (TI) India found that more than half of those surveyed had firsthand experience of paying bribe or peddling influence to get a job done in a public office.[156]
The Right to Information Act (2005) and equivalent acts in the Indian states, that require government officials to furnish information requested by citizens or face punitive action, computerisation of services and various central and state government acts that established vigilance commissions have considerably reduced corruption or at least have opened up avenues to redress grievances.[156] The 2009 report by Transparency International ranks India at 84th place and states that significant improvements were made by India in reducing corruption.[157][158]
[edit] Government

The current government has concluded that most spending fails to reach its intended recipients.[159] Lant Pritchett calls India's public sector "one of the world's top ten biggest problems — of the order of AIDS and climate change".[159] The Economist's 2008 article about the Indian civil service stated that the Indian central government employs around 3 million people, including "vast armies of paper-shuffling peons".[159]
At local level, administration can be worse. It is not unheard of that a majority of a state's assembly seats can be held by convicted criminals.[160] One study found that 25% of public sector teachers and 40% of public sector medical workers could not be found at the workplace. India's absence rates are one of the worst in the world.[161][162][163][164]
[edit] Education
India has made huge progress in terms of increasing primary education attendance rate and expanding literacy to approximately two thirds of the population.[165] The right to education at elementary level has been made one of the fundamental rights under the Eighty-Sixth Amendment of 2002.[166] However, the literacy rate of 65% is still lower than the worldwide average and the country suffers from a high dropout rate.[167]
[edit] Infrastructure


Development of infrastructure was completely in the hands of the public sector and was plagued by corruption, bureaucratic inefficiencies, urban-bias and an inability to scale investment.[168] India's low spending on power, construction, transportation, telecommunications and real estate, at $31 billion or 6% of GDP in 2002 had prevented India from sustaining higher growth rates. This has prompted the government to partially open up infrastructure to the private sector allowing foreign investment[140][169][170] which has helped in a sustained growth rate of close to 9% for the past six quarters.[171]
Some 600 million Indians have no mains electricity at all.[172] While 80% of Indian villages have at least an electricity line, just 44% of rural households have access to electricity.[173] According to a sample of 97,882 households in 2002, electricity was the main source of lighting for 53% of rural households compared to 36% in 1993.[174] Some half of the electricity is stolen, compared with 3% in China. The stolen electricity amounts to 1.5% of GDP.[173][175] Almost all of the electricity in India is produced by the public sector. Power outages are common.[172] Many buy their own power generators to ensure electricity supply. As of 2005 the electricity production was at 661.6 billion kWh with oil production standing at 785,000 bbl/day. In 2007, electricity demand exceeded supply by 15%.[172] Multi Commodity Exchange has tried to get a permit to offer electricity future markets.[176]
Indian Road Network is developing. Trucking goods from Gurgaon to the port in Mumbai can take up to 10 days.[177] India has the world's third largest road network.[178] Container traffic is growing at 15% a year.[179] Some 60% of India's container traffic is handled by the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust in Navi Mumbai[citation needed]. Internet use is rare; there were only 7.57 million broadband lines in India in November 2009, however it is still growing at slower rate and is expected to boom after the launch of 3G and wimax services.[180]
Most urban cities have good water supply water 24 hours a day, while some smaller cities face water shortages in summer season. A World Bank report says it is an institutional problem in water agencies, or "how the agency is embedded in the relationships between politics and the citizens who are the consumers."[181]
[edit] Labour laws
India's labor regulations — among the most restrictive and complex in the world — have constrained the growth of the formal manufacturing sector where these laws have their widest application. Better designed labor regulations can attract more labor- intensive investment and create jobs for India's unemployed millions and those trapped in poor quality jobs. Given the country's momentum of growth, the window of opportunity must not be lost for improving the job prospects for the 80 million new entrants who are expected to join the work force over the next decade.
– World Bank: India Country Overview 2008.[150]
India's restrictive labor regulations hamper the large-scale creation of formal industrial jobs.[12][167][182]
India ranked 133th on the Ease of Doing Business Index 2010, behind countries such as China (89th), Pakistan (85th), and Nigeria (125th). The Constitution provides protection of child labour, slavory, equality of opportunities and forced labor etc. in form of fundamental rights, but the implementation of provisions cited is a big question mark.[183]
[edit] Economic disparities
Lagging states need to bring more jobs to their people by creating an attractive investment destination. Reforming cumbersome regulatory procedures, improving rural connectivity, establishing law and order, creating a stable platform for natural resource investment that balances business interests with social concerns, and providing rural finance are important.
– World Bank: India Country Overview 2008[150]
One of the critical problems facing India's economy is the sharp and growing regional variations among India's different states and territories in terms of per capita income, poverty, availability of infrastructure and socio-economic development.[185] Six low-income states - Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh - are home to more than half of India's population.[186]
Between 1999 and 2008, the annualized growth rates for Maharashtra (9%),[187] Gujarat (8.8%), Haryana (8.7%), or Delhi (7.4%) were much higher than for Bihar (5.1%), Uttar Pradesh (4.4%), or Madhya Pradesh (3.5%).[188] However, In 2009-10, Bihar witnessed a growth of about 12.6%, and ended up becoming the 'next big economy in india' , followed by Gujarat with a growth of 11.3% (Both are BJP-Ruled states).
Poverty rates in rural Orissa (43%) and rural Bihar (40%) are some of the worst in the world.[181] On the other hand, rural Haryana (5.7%) and rural Punjab (2.4%) compare well with middle-income countries.[181]
The five-year plans have attempted to reduce regional disparities by encouraging industrial development in the interior regions, but industries still tend to concentrate around urban areas and port cities[189] After liberalization, the more advanced states are better placed to benefit from them, with infrastructure like well developed ports, urbanisation and an educated and skilled workforce which attract manufacturing and service sectors. The union and state governments of backward regions are trying to reduce the disparities by offering tax holidays, cheap land, etc., and focusing more on sectors like tourism, which although being geographically and historically determined, can become a source of growth and is faster to develop than other sectors.[190][191]
[edit] Environment and health
On Yale and Columbia's Environmental Performance Index, India's score is 21/100 on sanitation, compared with 67/100 for the region and 48/100 for the country income group.[192]
[edit] See also
- Below Poverty Line (India)
- Bilateral investment treaty
- Indian Construction Industry
- Indian states ranking by families owning house
- List of companies of India
- Media of India
- Net international investment position
[edit] Notes
- ^ a b c d e "India". International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2010/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2007&ey=2010&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=534&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=81&pr.y=8. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ^ "Manufacturing helps GDP grow 7.4% in FY10". Economic Times.com. 31 May 2010. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/Manufacturing-helps-GDP-grow-74-in-FY10/articleshow/5996613.cms.
- ^ a b "India Minister: High Inflation Worrisome". WSJ.com. 2010-03-16. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704423504575211770915705064.html?mod=WSJ_business_EconomyNewsBucket. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ a b Poverty estimates for 2009-10, Planning commission, Government of India, April 2010. Accessed: 18 April 2010
- ^ Unemployment rate according to world CIA factbooks,CIA 1149,D. A.S Jadeja, December 2009
- ^ "External debt goes up marginally to $228 bn". Economic Times. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/External-debt-goes-up-marginally-to-228-bn/articleshow/5074272.cms.
- ^ Ralph Droms, Public dept of India as of 2009, December 2009.
- ^ "Field Listing :: Economic Aid - Recipient by country". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2064.html. Retrieved 2008-11-17.
- ^ "CIA — The World Factbook — Rank Order — GDP (purchasing power parity)". Cia.gov. 2009-03-05. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ^ "India Vision 2020" (PDF). http://planningcommission.gov.in/reports/genrep/pl_vsn2020.pdf. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ Eugene M. Makar (2007). An American's Guide to Doing Business in India.
- ^ a b c d e f "Economic survey of India 2007: Policy Brief" (PDF). OECD. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/17/52/39452196.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ a b "The India Report" (PDF). Astaire Research. http://www.ukibc.com/ukindia2/files/India60.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ a b c "India's Rising Growth Potential" (PDF). Goldman Sachs. 2007. http://www.usindiafriendship.net/viewpoints1/Indias_Rising_Growth_Potential.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Doing Business in India 2009". World Bank. http://www.doingbusiness.org/subnational/exploreeconomies/India2009.aspx. Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ "India now second fastest growing economy". Australiannews.net. http://www.australiannews.net/story/366072. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Maurice R. Landes (2009-12-17). "USDA - India". Ers.usda.gov. http://www.ers.usda.gov/Briefing/India/. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Marketing in the 21st Century: New world marketing - By Bruce David Keillor. Books.google.com. ISBN 9780275992767. http://books.google.com/books?id=4bXMvrwE_1EC&pg=PA82&dq=india+fastest+growing+economy&client=firefox-a. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "2009 MOSPI Official Press Release" (PDF). http://mospi.nic.in/PRESS_NOTE_Q1_31aug09.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India's fiscal deficit to be highest in the world: Goldman". Rediff.com. 2004-12-31. http://www.rediff.com/money/2009/feb/20bcrisis-india-fiscal-deficit-to-be-highest.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ http://www.business-standard.com/india/news/pmeac-for-including-expense-targets-in-fiscal-discipline/374074/ PMEAC for including expense targets in fiscal discipline
- ^ a b c d e f "CIA - The World Factbook - India". CIA. 2007-09-20. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html#Econ. Retrieved 2007-10-02.
- ^ a b "Country Profile: India" (PDF). Library of Congress - Federal Research Division. December 2004. http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/India.pdf. Retrieved 2007-06-24.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org. 2006-09-14. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2008&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=58&pr1.y=5&c=512%2C941%2C914%2C446%2C612%2C666%2C614%2C668%2C311%2C672%2C213%2C946%2C911%2C137%2C193%2C962%2C122%2C674%2C912%2C676%2C313%2C548%2C419%2C556%2C513%2C678%2C316%2C181%2C913%2C682%2C124%2C684%2C339%2C273%2C638%2C921%2C514%2C948%2C218%2C943%2C963%2C686%2C616%2C688%2C223%2C518%2C516%2C728%2C918%2C558%2C748%2C138%2C618%2C196%2C522%2C278%2C622%2C692%2C156%2C694%2C624%2C142%2C626%2C449%2C628%2C564%2C228%2C283%2C924%2C853%2C233%2C288%2C632%2C293%2C636%2C566%2C634%2C964%2C238%2C182%2C662%2C453%2C960%2C968%2C423%2C922%2C935%2C714%2C128%2C862%2C611%2C716%2C321%2C456%2C243%2C722%2C248%2C942%2C469%2C718%2C253%2C724%2C642%2C576%2C643%2C936%2C939%2C961%2C644%2C813%2C819%2C199%2C172%2C184%2C132%2C524%2C646%2C361%2C648%2C362%2C915%2C364%2C134%2C732%2C652%2C366%2C174%2C734%2C328%2C14 4%2C258%2C146%2C656%2C463%2C654%2C528%2C336%2C923%2C263%2C738%2C268%2C578%2C532%2C537%2C944%2C742%2C176%2C866%2C534%2C369%2C536%2C744%2C429%2C186%2C433%2C925%2C178%2C746%2C436%2C926%2C136%2C466%2C343%2C112%2C158%2C111%2C439%2C298%2C916%2C927%2C664%2C846%2C826%2C299%2C542%2C582%2C443%2C474%2C917%2C754%2C544%2C698&s=NGDPDPC&grp=0&a=. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org. 2006-09-14. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=22&pr.y=6&sy=2008&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=512%2C941%2C914%2C446%2C612%2C666%2C614%2C668%2C311%2C672%2C213%2C946%2C911%2C137%2C193%2C962%2C122%2C674%2C912%2C676%2C313%2C548%2C419%2C556%2C513%2C678%2C316%2C181%2C913%2C682%2C124%2C684%2C339%2C273%2C638%2C921%2C514%2C948%2C218%2C943%2C963%2C686%2C616%2C688%2C223%2C518%2C516%2C728%2C918%2C558%2C748%2C138%2C618%2C196%2C522%2C278%2C622%2C692%2C156%2C694%2C624%2C142%2C626%2C449%2C628%2C564%2C228%2C283%2C924%2C853%2C233%2C288%2C632%2C293%2C636%2C566%2C634%2C964%2C238%2C182%2C662%2C453%2C960%2C968%2C423%2C922%2C935%2C714%2C128%2C862%2C611%2C716%2C321%2C456%2C243%2C722%2C248%2C942%2C469%2C718%2C253%2C724%2C642%2C576%2C643%2C936%2C939%2C961%2C644%2C813%2C819%2C199%2C172%2C184%2C132%2C524%2C646%2C361%2C648%2C362%2C915%2C364%2C134%2C732%2C652%2C366%2C174%2C734%2C328%2C144% 2C258%2C146%2C656%2C463%2C654%2C528%2C336%2C923%2C263%2C738%2C268%2C578%2C532%2C537%2C944%2C742%2C176%2C866%2C534%2C369%2C536%2C744%2C429%2C186%2C433%2C925%2C178%2C746%2C436%2C926%2C136%2C466%2C343%2C112%2C158%2C111%2C439%2C298%2C916%2C927%2C664%2C846%2C826%2C299%2C542%2C582%2C443%2C474%2C917%2C754%2C544%2C698&s=PPPPC&grp=0&a=. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ ""Inclusive Growth and Service delivery: Building on India's Success"" (PDF). World Bank. 2006. http://siteresources.worldbank.org/SOUTHASIAEXT/Resources/DPR_FullReport.pdf. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
- ^ Corn & Glasserman 1999: Prologue
- ^ Donkin, Robin A. (August 2003). Between East and West: The Moluccas and the Traffic in Spices Up to the Arrival of Europeans. Diane Publishing Company. ISBN 0871692481.
- ^ Nehru, Jawaharlal (1946). Discovery of India. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-303103-1.
- ^ Kumar, Dharma (Ed.) (1982). The Cambridge Economic History of India (Volume 2) c. 1757 - c. 1970. Penguin Books. p. 519.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M. (2005). "2". Indian Economy. S.Chand. pp. 15–16. ISBN 81-219-0298-3.
- ^ Sankaran, S (1994). "3". Indian Economy: Problems, Policies and Development. Margham Publications. p. 50. ISBN.
- ^ Kumar, Dharma (Ed.). "4". The Cambridge Economic History of India (Volume 2). p. 422.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "2". Indian Economy. p. 16.
- ^ "Economy of Mughal Empire". Bombay Times (Times of India). 2004-08-17.
- ^ Kumar, Dharma (Ed.). "1". The Cambridge Economic History of India (Volume 2). pp. 32–35.
- ^ "Ch20". Unu.edu. http://www.unu.edu/unupress/unupbooks/80815e/80815E0k.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ^ Jain, TR; Ohri, VK. Economics - Google Books. Books.google.com. ISBN 9788187344346. http://books.google.com/books?id=XdEpABrFW8QC&pg=PA20&dq=british+india+handicrafts+raj&client=firefox-a#PPA21,M1. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ The rise and fall of British India ... - Google Books. Books.google.com. ISBN 9780416335309. http://books.google.com/books?id=rMoOAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA186&dq=british+india+economy&lr=&client=firefox-a. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Of Oxford, economics, empire, and freedom". The Hindu. 2 October 2005. http://www.hindu.com/2005/07/10/stories/2005071002301000.htm.
- ^ a b Williamson, John and Zagha, Roberto (2002) (PDF). From the Hindu Rate of Growth to the Hindu Rate of Reform. Working Paper No. 144. Center for research on economic development and policy reform. http://scid.stanford.edu/pdf/credpr144.pdf.
- ^ Roy, Tirthankar (2000). "1". The Economic History of India. Oxford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 0-19-565154-5.
- ^ Roy, Tirthankar (2000). "10". The Economic History of India. Oxford University Press. p. 304. ISBN 0-19-565154-5.
- ^ Kelegama, Saman and Parikh, Kirit (2000). Political Economy of Growth and Reforms in South Asia. Second Draft. http://www.eldis.org/static/DOC12473.htm.
- ^ Sam Staley (2006). "The Rise and Fall of Indian Socialism: Why India embraced economic reform". http://www.reason.com/news/show/36682.html.
- ^ Street Hawking Promise Jobs in Future, The Times of India, 2001-11-25
- ^ Cameron, John and Ndhlovu, P Tidings (2001) (PDF). Cultural Influences on Economic Thought in India: Resistance to diffusion of neo-classical economics and the principles of Hinduism. Archived from the original on 2006-08-23. http://web.archive.org/web/20060823161225/http://www.economicissues.org/archive/pdfs/5v6p2.PDF.
- ^ "Milton Friedman on the Nehru/Mahalanobis Plan". http://www.indiapolicy.org/debate/Notes/fried_opinion.html. Retrieved 2005-07-16.
- ^ "MBA global Top 100 rankings - FT". ft.com. http://rankings.ft.com/businessschoolrankings/global-mba-rankings. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ^ Ghosh, Arunabha (2004-06-01) (PDF). India's pathway through economic crisis(which makes failer of mixed economy). Global Economic Governance Programme GEG Working Paper 2004/06. http://www.globaleconomicgovernance.org/wp-content/uploads/Ghosh%20-%20India.pdf. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Economic reforms in India: Task force report" (PDF). 2006. http://harrisschool.uchicago.edu/News/press-releases/IPP%20Economic%20Reform%20in%20India.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ Panagariya, Arvind (2004). India in the 1980s and 1990s: A Triumph of Reforms. http://ideas.repec.org/p/wpa/wuwpit/0403005.html.
- ^ "That old Gandhi magic". The Economist. 27 November 1997. http://www.economist.com/world/asia/displaystory.cfm?story_id=107076.
- ^ "Moody's upgrade — Uplifts the mood but raises questions". Business Line. http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/2003/02/10/stories/2003021000040900.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ^ Wilson, Dominic; Purushothaman, Roopa (2003-10-01). "DreamingWith BRICs: The Path to 2050" (PDF). Global economics paper No. 99. Goldman Sachs. http://www2.goldmansachs.com/insight/research/reports/99.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ Grammaticas, Damian (2007-01-24). ""Indian economy 'to overtake UK'"". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/south_asia/6294409.stm. Retrieved 2007-01-26.
- ^ "IMF Announces Sale of 200 metric tons of Gold to the Reserve Bank of India". International Monetary Fund. 2009-11-02. http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2009/pr09381.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ "Asian countries lead list of top outsourcing destinations". Bleum.com. 2007-03-27. http://www.bleum.com/xweb/topoutsourcing.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Sheth, Niraj (2009-05-28). "Outsourcing Statistics - 2009 Black Book of Outsourcing". Online.wsj.com. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB124344190542659025.html#project%3DOUTSOURCING09%26articleTabs%3Dinteractive. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Tyres & Accessories". Reifenpresse.de. http://www.reifenpresse.de/CDML007/en/gast/detail.php?tk=&t=unt&RecID=7767&wert1=19843&wert2=. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "The small car dream-merchants- Tata's People's Car-Specials-The Economic Times". Economictimes.indiatimes.com. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/2682810.cms. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ a b "The Next People's Car". forbes.com. http://www.forbes.com/home/free_forbes/2007/0416/070.html. Retrieved 2008-01-21.
- ^ "Census Reference Tables B-Series Economic Tables". Censusindia.gov.in. http://www.censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/Census_data_finder/B_Series/Industrial_Category_of_worker.htm. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ Please see the sources for the List of countries by GDP sector composition. The data is compiled through CIA World Factbook figures.
- ^ "Economic structure". The Economist. 6 October 2003. http://www.economist.com/countries/India/profile.cfm?folder=Profile%2DEconomic%20Structure.
- ^ "Indian manufacturers learn to compete". The Economist. 12 February 2004. http://www.economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%27%298%3C%2FPQ%3B%21%21P%214%0A.
- ^ "Industry Overview — Indian Overview". http://www.citiindia.com/indian_overview.asp?pgname=Overview.
- ^ "Helping Tirupur emerge as a leader in knitwear exports in India — Tiruppur". The Hindu. http://www.thehindu.com/2007/06/11/stories/2007061110090500.htm.
- ^ "The Coming Death Of Indian Outsourcing". Forbes. 2008-02-29. http://www.forbes.com/home/enterprisetech/2008/02/29/mitra-india-outsourcing-tech-enter-cx_sm_0229outsource.html.
- ^ Sheth, Niraj (2009-05-28). "Outlook for Outsourcing - WSJ". Online.wsj.com. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB124344190542659025.html#project%3DOUTSOURCING09%26articleTabs%3Dinteractive. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India's Revenue From Outsourcing Could Be $225B in 2020". Pcworld.com. http://www.pcworld.com/businesscenter/article/163513/indias_revenue_from_outsourcing_could_be_225b_in_2020.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ a b "Retailing in India Unshackling the chain stores". Economist. 2008. http://www.economist.com/displayStory.cfm?story_id=11465586.
- ^ Mudur, Ganapati (June 2004). "Hospitals in India woo foreign patients". British Medical Journal 328 (7452): 1338. doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7452.1338. PMID 15178611.
- ^ "archives". Taipei Times. 2008-03-29. http://www.taipeitimes.com/News/worldbiz/archives/2008/03/29/2003407560. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ http://www.irri.org/science/ricestat/data/may2008/WRS2008-Table07.pdf
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "28". Indian Economy. pp. 485–491.
- ^ Agribusiness in India UK India Business Council, retrieved on December 2009
- ^ Lester R. Brown World's Rangelands Deteriorating Under Mounting Pressure Earth Policy Institute, Retrieved on- February 2008
- ^ a b c Indian agriculture Agribusiness Information Centre, Retrieved on- February 2008
- ^ "Major Food And Agricultural Commodities And Producers - Countries By Commodity". Fao.org. http://www.fao.org/es/ess/top/commodity.html?lang=en&item=1185&year=2005. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Silk city to come up near B'lore". Deccanherald.com. 2009-10-17. http://www.deccanherald.com/content/31009/silk-city-come-up-near.html. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Silk export likely to be Rs 7,000 cr by 2012: Minister". Sify.com. 2009-07-15. http://sify.com/finance/fullstory.php?a=jhpsgPhcaaa&title=Silk_export_likely_to_be_Rs_7%2C000_cr_by_2012%3A_Minister. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ Old private banks are private banks existing prior to opening up of the banking sector.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "50". Indian Economy. pp. 847–850.
- ^ Ghosh, Jayati. "Bank Nationalisation: The Record". Macroscan. http://www.macroscan.com/cur/jul05/cur210705Bank_Nationalisation.htm. Retrieved 2005-08-05.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "50". Indian Economy. pp. 850–851.
- ^ India growth story is attracting talent from govt establishments HT media, Retrieved on- December 2007
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "50". Indian Economy. pp. 865–867.
- ^ Diana Farrell and Susan Lund. "Reforming India's Financial System" (PDF). http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/APCITY/UNPAN028982.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "The Hindu : Kerala / Kochi News : Diversify fishing methods, says Pawar". Hindu.com. http://www.hindu.com/2008/01/05/stories/2008010552830300.htm. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "Total > Coal Proved Reserves statistics - countries compared". NationMaster. 2009-10-31. http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/ene_coa_pro_res_tot-energy-coal-proved-reserves-total. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ "Uranium shortage holding back India's nuclear power drive". Livemint.com. 2008-06-30. http://www.livemint.com/2008/06/30222448/Uranium-shortage-holding-back.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Bush signs India-US nuclear deal into law". Livemint.com. 2008-10-09. http://www.livemint.com/2008/10/09005930/Bush-signs-IndiaUS-nuclear-de.html?d=1. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "China, India stoke energy bond". Chinadaily.com.cn. http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/opinion/2010-02/02/content_9411882.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Datt, Mihir Bhojani & Vivek Sundharam, K.P.M.. "7". Indian Economy. pp. 90,97,98,100.
- ^ "India's energy security challenge". Iags.org. 2004-01-21. http://www.iags.org/n0121043.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Indian Oil and Natural Gas". Indianchild.com. http://www.indianchild.com/india_oil_and_natural_gas.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Harrison, Michael (2006-11-24). "Petronas takes key stake in Cairn before £3.6bn Indian float". London: Independent.co.uk. http://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/news/petronas-takes-key-stake-in-cairn-before-16336bn-indian-float-425619.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India 2008/09 oil import growth lowest in 3 yrs | Business News | Reuters". In.reuters.com. 2009-04-24. http://in.reuters.com/article/businessNews/idINIndia-39236620090424. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Reliance Net Beats Estimate After Boosting Natural Gas Sales". BusinessWeek. 2010-01-27. http://www.businessweek.com/news/2010-01-27/reliance-net-beats-estimate-after-boosting-natural-gas-sales.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India's March Exports Grow 26.6%". Bloomberg.com. http://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601091&sid=aoMZPHuRqWc0&refer=india. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Resilient India - By Shashi Tharoor". Realclearworld.com. 2009-03-24. http://www.realclearworld.com/articles/2009/03/this_is_quite_a_turnabout.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ India says export growth will continue to slow[dead link]
- ^ Srinivasan, T.N. (2002) (PDF). Economic Reforms and Global Integration. 17 January 2002. http://www.econ.yale.edu/%7Esrinivas/ec_reforms.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "46". Indian Economy. pp. 767,772–76.
- ^ "INDIA'S FOREIGN TRADE: APRIL-DECEMBER, 2007". Commerce.nic.in. http://commerce.nic.in/tradestats/indiatrade_press.asp. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Ministry of Commerce, Government of India - Imports and Exports Databank". Commerce.nic.in. http://commerce.nic.in/eidb/default.asp. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India & the World Trade Organization". http://www.indianembassy.org/policy/WTO/overview.html. Retrieved 2005-07-09.
- ^ Agencies (2008-07-02). "Oil prices to dent India's balance sheet: Goldman Sachs". Expressindia.com. http://www.expressindia.com/latest-news/Oil-prices-to-dent-India--s-balance-sheet--Goldman-Sachs/330411/. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Research and Markets: The Total Crude Oil Import in India". Reuters.com. 2009-02-04. http://www.reuters.com/article/pressRelease/idUS196866+04-Feb-2009+BW20090204. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ a b "India's exports continue to fall". BBC News. 2009-07-01. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/8128449.stm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Chaturvedi, Neelabh (2009-08-27). "India Cuts Export Aim, Seeks Solace in New Markets". Online.wsj.com. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB125135625520662979.html?mod=googlenews_wsj. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "India`s external debt rises to US$190.5bn". Indiainfoline.com. http://www.indiainfoline.com/news/innernews.asp?storyId=55091&lmn=1. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ anurag. "External Commercial Borrowings". Banknetindia.com. http://www.banknetindia.com/banking/ecb.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "FDI in India Statistics". http://dipp.nic.in/fdi_statistics/india_fdi_index.htm. Retrieved 2008-02-12.
- ^ Much of India's FDI is routed through Mauritius, because both countries have an agreement to avoid double taxation. "India to sign free trade agreement with Mauritius". http://www.bilaterals.org/article.php3?id_article=1521. Retrieved 2005-08-15.
- ^ a b "India 2nd best country for biz investment: Survey — The Financial Express". Financialexpress.com. http://www.financialexpress.com/news/India-2nd-best-country-for-biz-investment-Survey/343344/. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "Next Big Spenders: India's Middle Class". Mckinsey.com. http://www.mckinsey.com/mgi/mginews/bigspenders.asp. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "The Hinduonline". Hindu.com. 2005-02-25. http://www.hindu.com/2005/02/25/stories/2005022506990100.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Hindustan Times ''India attracts $ 25 billion FDI in 2007-08''". Hindustantimes.com. 2008-05-20. http://www.hindustantimes.com/StoryPage/StoryPage.aspx?id=54c00804-3161-4609-ad33-b5307f3c1b2e&ParentID=6d35884a-76ac-433c-af16-ccc72908c3e5&MatchID1=4689&TeamID1=4&TeamID2=1&MatchType1=1&SeriesID1=1182&PrimaryID=4689&Headline=India+attracts+%24+25+billion+FDI+in+2007-08. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Economic Times ''FDI inflows to exceed $35 billion target in 2008-09''". Economictimes.indiatimes.com. 2008-08-17. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/Economy/FDI_to_exceed_USD_35_bn_in_08-09/articleshow/3373887.cms. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ [Indian Economic Superpower: Fiction or Future? edited by Jayashankar M. Swaminathan, World Scientific Publishing, 2008]
- ^ "U.S. Dollar to Indian Rupee Exchange Rate". http://www.oanda.com/currency/historical-rates?date_fmt=us&date=02/03/10&date1=01/28/10&exch=USD&expr=INR&expr2=INR&format=HTML&margin_fixed=0. Retrieved 2010-02-03.
- ^ "RBI". RBI. http://www.rbi.org.in/currency/coins.html. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ^ a b c d "The developing world is poorer than we thought, but no less successful in the fight against poverty". World Bank. 2008. http://econ.worldbank.org/external/default/main?pagePK=64165259&piPK=64165421&theSitePK=469372&menuPK=64166093&entityID=000158349_20080826113239.
- ^ "One-third of world's poor in India: Survey-India-The Times of India". Timesofindia.indiatimes.com. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/India/One-third_of_worlds_poor_in_India/articleshow/3409374.cms. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "The Hindu : National : World Bank's new poverty norms find larger number of poor in India". Thehindu.com. http://www.thehindu.com/2008/08/28/stories/2008082856061300.htm. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "Define poverty anew- Opinion-The Economic Times". Economictimes.indiatimes.com. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/Editorials/Define_poverty_anew/articleshow/3423435.cms. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ Steve Schifferes (27 August 2008). "BBC NEWS | Business | World poverty 'more widespread'". News.bbc.co.uk. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/7583719.stm. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ "India has fewer poor people: World Bank". Business Standard. http://www.business-standard.com/india/storypage.php?autono=332669.
- ^ "Bicycle Ownership in India". http://www.bike-eu.com/news/1573/bicycle-ownership-in-india.html.
- ^ a b "33% of Indians live in less space than US prisoners". Times of India. 2008. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/33_of_Indians_live_in_less_space_than_US_prisoners/articleshow/3753189.cms.
- ^ "India: Undernourished Children: A Call for Reform and Action". World Bank. http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/SOUTHASIAEXT/0,,contentMDK:20916955~pagePK:146736~piPK:146830~theSitePK:223547,00.html.
- ^ "Malnutrition Among Indian Children Worse Than in Sub-Saharan Africa". Medindia. http://www.medindia.net/news/Malnutrition-Among-Indian-Children-Worse-Than-in-Sub-Saharan-Africa-30955-1.htm.
- ^ This figure is extremely sensitive to the surveying methodology used. The Uniform Recall Period (URP) gives 27.5%. The Mixed Recall Period (MRP) gives a figure of 21.8%
- ^ "Microsoft Word - Press Release - March 2007-Approved.doc" (PDF). http://www.planningcommission.gov.in/news/prmar07.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "NCEUS Report" (PDF). http://nceus.gov.in/Condition_of_workers_sep_2007.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Nearly 80% of India Lives On Half Dollar A Day". Reuters. 10 August 2007. http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSDEL218894. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
- ^ a b c d "Economic Survey 2004–2005". http://indiabudget.nic.in/es2004-05/esmain.htm. Retrieved 2006-07-15.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "22". Indian Economy. pp. 367,369,370.
- ^ "Jawahar gram samriddhi yojana". http://rural.nic.in/jgsyg.htm. Retrieved 2005-07-09.
- ^ a b c "Growing Unemployment Problem in India" (PDF). http://newsgroups.derkeiler.com/pdf/Archive/Soc/soc.culture.pakistan/2008-09/msg00054.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ Why India needs labour law reform. BBC
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "24". Indian Economy. pp. 403–405.
- ^ Embassy of India. "Child Labor and India — Embassy of India". Indianembassy.org. http://www.indianembassy.org/policy/Child_Labor/childlabor.htm#intro. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ^ "Remittances from Indians abroad push India to the top". 2007. http://www.nrirealtynews.com/stories/oct07/remittances-from-indians-abroad-push-india-to-top.php.
- ^ Marketing in the 21st Century: New world marketing - By Bruce David Keillor. Books.google.com. ISBN 9780275992767. http://books.google.com/books?id=4bXMvrwE_1EC&pg=PA83&dq=india+fastest+growing+middle+class&as_brr=3&client=firefox-a. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "The top 10 challenges for India". Rediff. http://specials.rediff.com/money/2008/jun/17slid01.htm.
- ^ a b c "India Country Overview 2008". World Bank. 2008. http://www.worldbank.org.in/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/SOUTHASIAEXT/INDIAEXTN/0,,contentMDK:20195738~menuPK:295591~pagePK:141137~piPK:141127~theSitePK:295584,00.html.
- ^ a b "India: Priorities for Agriculture and Rural Development". World Bank. http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/SOUTHASIAEXT/EXTSAREGTOPAGRI/0,,contentMDK:20273764~menuPK:548214~pagePK:34004173~piPK:34003707~theSitePK:452766,00.html.
- ^ Multiple authors (2004). Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2004. http://dacnet.nic.in/eands/4.6(a)All%20lndia%20Area,%20Production%20and%20Yield%20of%20Rice.xls.
- ^ Sankaran, S. "28". Indian Economy: Problems, Policies and Development. pp. 492–493.
- ^ Sengupta, Somini (22 June 2008). "The Food Chain in Fertile India, Growth Outstrips Agriculture". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/06/22/business/22indiafood.html?_r=1. Retrieved 2010-03-29.
- ^ "India on the Move". India Reborn. 2009-02-17. No. 2, season 1.
- ^ a b Transparency International India. "India Corruption Study 2005" (PDF). Centre for Media Studies. http://www.cmsindia.org/cms/events/corruption.pdf. Retrieved 2008-03-14.
- ^ "2009 Corruption Perceptions Index reinforces link between poverty and corruption". Transparency International. http://www.transparency.org/policy_research/surveys_indices/cpi/2009/cpi_2009_table. Retrieved 2008-03-15.
- ^ "CPI Table". Transparency International. http://www.transparency.org/policy_research/surveys_indices/cpi/2009/cpi_2009_table. Retrieved 2008-03-15.
- ^ a b c India's civil service: Battling the babu raj 6 March 2008 The Economist
- ^ The criminalisation of Indian democracy (2 May 2007). "Jo Johnson". Financial Times. http://www.ft.com/cms/s/21d0f5f8-f8c1-11db-a940-000b5df10621.html. Retrieved 2007-05-12.
- ^ "Teachers and Medical Worker Incentives in India by Karthik Muralidharan" (PDF). http://econ.ucsd.edu/~kamurali/teachers%20and%20medical%20worker%20incentives%20in%20india.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ Combating India's truant teachers. BBC
- ^ Private Schools in Rural India: Some Facts (presentation) / Public and Private Schools in Rural India (a paper). Karthik Muralidharan, Michael Kremer.
- ^ "Teacher absence in India: A snapshot" (PDF). http://globetrotter.berkeley.edu/macarthur/inequality/papers/KremerTeacherAbsenceinIndia.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Education in India". World Bank. http://www.worldbank.org.in/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/SOUTHASIAEXT/INDIAEXTN/0,,contentMDK:21493265~pagePK:141137~piPK:141127~theSitePK:295584,00.html.
- ^ 86th Amendment Act, 2002.
- ^ a b "A special report on India: An elephant, not a tiger". Economist. 11 December 2008. http://www.economist.com/specialreports/displayStory.cfm?story_id=12749735.
- ^ Sankaran, S (1994). Indian Economy: Problems, Policies and Development. Margham Publications. ISBN.
- ^ "Infrastructure the missing link". CNN. 2004-10-06. http://edition.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/asiapcf/09/03/india.eye.infra/. Retrieved 2005-08-14.
- ^ "Infrastructure in India: Requirements and favorable climate for foreign investment". http://www.asiatradehub.com/india/intro.asp. Retrieved 2005-08-14.
- ^ "India's Economic Growth Unexpectedly Quickens to 9.2%". Bloomberg. http://bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601087&sid=ayAK98NMbmCA&refer=home.
- ^ a b c "A special report on India: Creaking, groaning: Infrastructure is India's biggest handicap". The Economist. 11 December 2008. http://www.economist.com/specialreports/displaystory.cfm?story_id=12749787.
- ^ a b "Reforming the Power Sector: Controlling Electricity Theft and Improving Revenue" (PDF). The World Bank. http://rru.worldbank.org/documents/publicpolicyjournal/272bhatia_Gulati.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Housing condition in India: Household amenities and other characteristics (July — September 2002)". Government of India. http://www.mospi.nic.in/nss_58round_press_note_6june05.htm.
- ^ "India struggles with power theft". BBC. 2006-03-15. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4802248.stm. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ^ "MCX move to launch electricity future faces legal hurdle". The Financial Express. http://www.financialexpress.com/news/mcx-move-to-launch-electricity-future-faces-legal-hurdle/401592/.
- ^ "The Trouble With India: Crumbling roads, jammed airports, and power blackouts could hobble growth". BusinessWeek. 19 March 2007. http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/content/07_12/b4026001.htm.
- ^ "Infrastructure Rankings". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2085rank.html.
- ^ "Ageing Indian infrastructure causes congestion". The Age. 2005. http://www.theage.com.au/news/business/ageing-indian-infrastructure-causes-congestion/2005/09/21/1126982123165.html.
- ^ "Tele-base soars to 543m as mobile cos add record 17.65m in Nov" (doc). Economic Times. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/News/News-By-Industry/Telecom/Tele-base-soars-to-543m-as-mobile-cos-add-record-1765m-in-Nov/articleshow/5370510.cms. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ^ a b c "Development Policy Review". World Bank. http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/SOUTHASIAEXT/0,,contentMDK:20980493~pagePK:146736~piPK:146830~theSitePK:223547,00.html.
- ^ "Why India needs labour law reform". BBC. 2005-06-27. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4103554.stm. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ^ [Sapovadia, Vrajlal K. and Mattioli, Maria C., Laws of Labor: Core Labor Standards and Global Trade. International Trade, Vol. 26, No. 2, June 2004. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=711542]
- ^ "BBC News Online | Business | Winners and losers as India booms". News.bbc.co.uk. 2007-05-21. http://news.bbc.co.uk/nolpda/ukfs_news/hi/newsid_6677000/6677645.stm. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ^ Datt, Ruddar & Sundharam, K.P.M.. "27". Indian Economy. pp. 471–472.
- ^ "Country Strategy for India (CAS) 2009-2012" (PDF). World Bank. http://www.ukibc.com/ukindia2/files/India60.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Maharashtra poised for 9 percent growth in 2007-08". Thaindian.com. 2008-03-18. http://www.thaindian.com/newsportal/business/maharashtra-poised-for-9-percent-growth-in-2007-08_10028858.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "A special report on India: Ruled by Lakshmi". The Economist. 11 December 2008. http://www.economist.com/surveys/displaystory.cfm?story_id=12749719&fsrc=rss.
- ^ Bharadwaj, Krishna (1991). "Regional differentiation in India". in Sathyamurthy, T.V. (ed.). Industry & agriculture in India since independence. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–199. ISBN 0-19-564394-1.
- ^ Sachs, D. Jeffrey; Bajpai, Nirupam and Ramiah, Ananthi (2002) (PDF). Understanding Regional Economic Growth in India. Working paper 88. Archived from the original on 2007-07-01. http://web.archive.org/web/20070701042205/http://www2.cid.harvard.edu/cidwp/088.pdf.
- ^ Kurian, N.J.. "Regional disparities in india". http://planningcommission.nic.in/reports/sereport/ser/vision2025/regdsprty.doc. Retrieved 2005-08-06.
- ^ SPECIAL REPORT: Putrid Rivers Of Sludge: Delhi's bureaucrats bicker over cholera and the role of city drains and state sewers. NewsWeek on July 7–14, 2008 issue
[edit] References
Books- Alamgir, Jalal (2008). India's Open-Economy Policy. Routledge. ISBN 9780415776844.
- Bharadwaj, Krishna (1991). "Regional differentiation in India". in Sathyamurthy, T.V. (ed.). Industry & agriculture in India since independence. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–199. ISBN 0195643941.
- Kumar, Dharma (Ed.) (1982). The Cambridge Economic History of India (Volume 2) c. 1757 - c. 1970. Penguin Books.
- Nehru, Jawaharlal (1946). Discovery of India. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-303103-1.
- Roy, Tirthankar (2000). The Economic History of India. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-565154-5.
- Sankaran, S (1994). Indian Economy: Problems, Policies and Development. Margham Publications.
- Bernardi, Luigi and Fraschini, Angela (2005). Tax System And Tax Reforms In India. Working paper n. 51. http://ideas.repec.org/p/uca/ucapdv/45.html.
- Centre for Media Studies (2005) (PDF). India Corruption Study 2005: To Improve Governance Volume – I: Key Highlights. Transparency International India. http://www.prajanet.org/newsroom/internal/tii/ICS2k5_Vol1.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- Ghosh, Jayati. "Bank Nationalisation: The Record". Macroscan. http://www.macroscan.com/cur/jul05/cur210705Bank_Nationalisation.htm. Retrieved 2005-08-05.
- Gordon, Jim and Gupta, Poonam (2003) (PDF). Understanding India's Services Revolution. 12 November 2003. http://www.imf.org/external/np/apd/seminars/2003/newdelhi/gordon.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- Kelegama, Saman and Parikh, Kirit (2000). Political Economy of Growth and Reforms in South Asia. Second Draft. http://www.eldis.org/static/DOC12473.htm.
- Panagariya, Arvind (2004). India in the 1980s and 1990s: A Triumph of Reforms. http://ideas.repec.org/p/wpa/wuwpit/0403005.html.
- Rodrik, Dani and Subramanian, Arvind (2004) (PDF). From "Hindu Growth" To Productivity Surge: The Mystery Of The Indian Growth Transition. http://ksghome.harvard.edu/~drodrik/IndiapaperdraftMarch2.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- Sachs, D. Jeffrey; Bajpai, Nirupam and Ramiah, Ananthi (2002) (PDF). Understanding Regional Economic Growth in India. Working paper 88. Archived from the original on 2007-07-01. http://web.archive.org/web/20070701042205/http://www2.cid.harvard.edu/cidwp/088.pdf.
- Srinivasan, T.N. (2002) (PDF). Economic Reforms and Global Integration. 17 January 2002. http://www.econ.yale.edu/%7Esrinivas/ec_reforms.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- Williamson, John and Zagha, Roberto (2002) (PDF). From the Hindu Rate of Growth to the Hindu Rate of Reform. Working Paper No. 144. Center for research on economic development and policy reform. http://scid.stanford.edu/pdf/credpr144.pdf.
- "Economic Survey 2004–2005". http://indiabudget.nic.in/es2004-05/esmain.htm. Retrieved 2005-07-15.
- "History of the Planning Commission". http://planningcommission.nic.in/aboutus/history/about.htm. Retrieved 2005-07-22.
- "India & the World Trade Organization". http://www.indianembassy.org/policy/WTO/overview.html. Retrieved 2005-07-09.
- "Jawahar gram samriddhi yojana". http://rural.nic.in/jgsyg.htm. Retrieved 2005-07-09.
- Kurian, N.J.. "Regional disparities in india". http://planningcommission.nic.in/reports/sereport/ser/vision2025/regdsprty.doc. Retrieved 2005-08-06.
- Multiple authors (2004) (PDF). Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2004. http://agricoop.nic.in/statatglance2004/AtGlance.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- "That old Gandhi magic". The Economist. 27 November 1997. http://economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%26%29H%2C%2BPQ%27%25%0A.
- "Indif_real_GDP_per_capitaa says 21 of 29 states to launch new tax". Daily Times. 25 March 2005. http://www.dailytimes.com.pk/default.asp?page=story_25-3-2005_pg5_13.
- "Economic structure". The Economist. 6 October 2003. http://www.economist.com/countries/India/profile.cfm?folder=Profile%2DEconomic%20Structure.
- "Indian manufacturers learn to compete". The Economist. 12 February 2004. http://www.economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%27%298%3C%2FPQ%3B%21%21P%214%0A.
- "India's next 50 years". The Economist. 14 August 1997. http://economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%26%29H8%2FRQ%3B%22%0A.
- "The plot thickens". The Economist. 31 May 2001. http://economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%26%288%20%2BRQ%3F%24%0A.
- "The voters' big surprise". The Economist. 13 May 2004. http://economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=S%27%2984%2BRQ3%2B%21%40%20%2C%0A.
- "Regional stock exchanges – Bulldozed by the Big Two". http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/businessline/2001/07/20/stories/042062cr.htm. Retrieved 2005-08-10.
- "Infrastructure the missing link". CNN. 2004-10-06. http://edition.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/asiapcf/09/03/india.eye.infra/. Retrieved 2005-08-14.
- "Of Oxford, economics, empire, and freedom". The Hindu. 2 October 2005. http://www.hindu.com/2005/07/10/stories/2005071002301000.htm.
- [Media:Economic Development of India.pdf "Economic Development of India"] (PDF). Media:Economic Development of India.pdf. Retrieved 17 May 2007.
- "Milton Friedman on the Nehru/Mahalanobis Plan". http://www.indiapolicy.org/debate/Notes/fried_opinion.html. Retrieved 2005-07-16.
- "Forex reserves up by $88 mn". http://www.business-standard.com/bsonline/storypage.php?bKeyFlag=BO&autono=9047. Retrieved 2005-08-10.
- "CIA — The World Factbook". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html. Retrieved 2005-08-02.
- "Infrastructure in India: Requirements and favorable climate for foreign investment". http://www.asiatradehub.com/india/intro.asp. Retrieved 2005-08-14.
[edit] External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Economy of India |
| Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: Economy of India |
- Finance Ministry of India
- India in Business- Official website for Investment and Trade in India
- Reserve Bank of India's database on the Indian economy
- World Bank - India Country Overview
- Ernst & Young 2006 report on doing Business in India
- CIA - The World Factbook – India
- India Economic Scan
- Will India Become a Superpower? Here are 12 Hints
| |||||
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIL ready to supply gas to ADAG plants 18 Jun 2010, 1136 hrs IST,PTI
| |||||||||||||||||||
| 0314 hrs IST 0341 hrs IST 0046 hrs IST 0101 hrs IST 0052 hrs IST 0159 hrs IST 0204 hrs IST 0101 hrs IST 0118 hrs IST 0227 hrs IST 0227 hrs IST | |||||||||||||||||||
| World Bank says China's economy slowing World Bank said, China needs to rebalance growth away from investment, while remaining flexible and urged greater flexibility in interest rates. | |||||||||||||||||||
| DTC: Impact on retirement benefits & property income Check out the impact of revised DTC on retirement benefits, house property income, capital gains & wealth-tax. Decoding Direct Tax Code | DTC: Impact on common man | |||||||||||||||||||
| All headlines >> | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Politics / Nation
| Opinion
| ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodities  Farmers bet on rains Farmers bet on rainsWith a normal monsoon forecast every state has increased its estimates. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Smart Living | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ET on mobile | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ePaper: Print Edition  Get the replica of your favourite edition of Economic Times Feel at home.. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zigwheels New | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Online food guides at timescity.com | ||||||||||||||||||||
Palash Biswas
http://www.bangaindigenous.blogspot.com/
http://www.troubledgalaxydetroyeddreams.blogspot.com/
























 News, Business, Stocks & more via 58888
News, Business, Stocks & more via 58888 





No comments:
Post a Comment